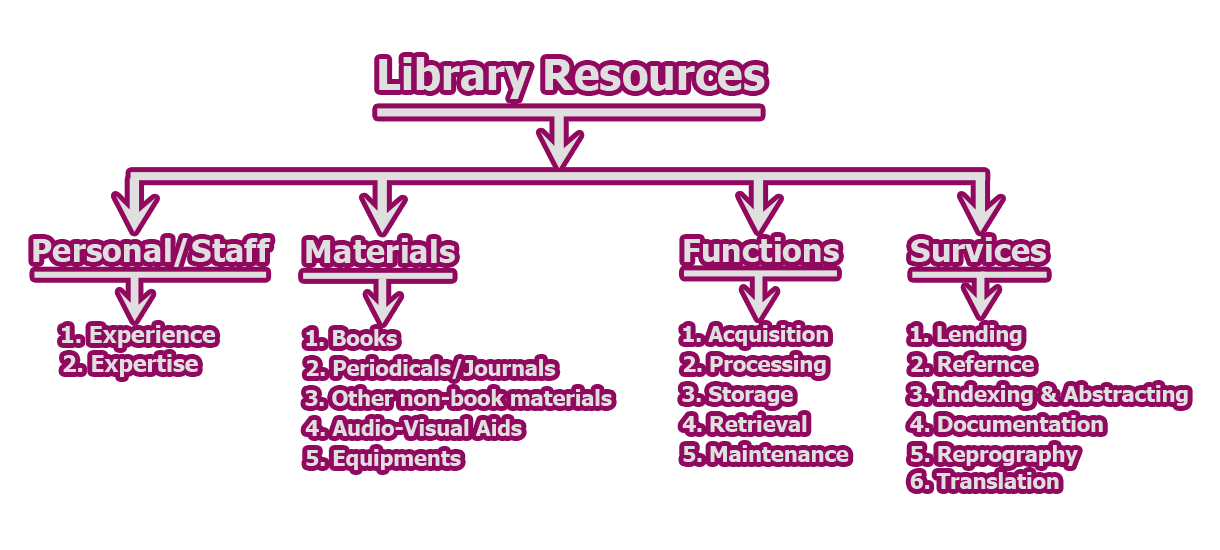
Categories of Library Resources:
The term ‘Library Resources’ means any and all the materials, functions, and services which constitute a modern library system. We may categories of library resources by the following chart:
- Library Staff/Personnel: The resources of any library must include the experience and expertise of the professional and non-professional staff who engaged in decision making work, technical work, reference service, documentation service, and other library operational services.
- Library Materials: Materials means all type of equipment printed and non-printed may be the resources of library and information center. Besides the traditional materials, some non-traditional items like microforms, films, and machine-readable database, CD-ROM etc. are also considered as library materials.
- Library Functions: Functions indicate those activities that are required to purchase/acquire/procure, process, store and retrieve library materials.
- Library Services: By service we mean those activities and procedures used to relate the users to the materials.
So, library resources are the amalgamation of people, process, ideas, materials and money which form the substance of library.
Factors and Processes for the development of library’s information resources:
Some factors and processes have to consider in library’s information resource development of a library which are being:
- Survey of the library’s own resource: The primary element in developing any collection in a preliminary survey of the resources, which the library already possesses. The book selector must discover what basic books and other materials are already in the library. For this the collection is to be checked against the bibliographies of good standard histories of the particular subject considered.
- Updating the Collection: The existing collection of the library should be updated. In updating the collection, the selection of current resource should be accompanied by weeding or discarding unwanted resources, duplicating of titles as well as of replacement of lost or worn-out materials.
- Variety of Materials: According to the clientele choice most current materials, order books and out-of-print title may be selected and purchased on the most convenient terms possible. The traditional resource should be supplemented/added by selection of government documents, technical and scientific reports and pamphlets etc.
- Gifts: In developing the collection gifts should be accepted only in the case they add strength to the library collection and do not carry unreasonable restriction. A policy should be developed for the library concerned and why such gift should be integrated with the regular collection and where the gifts are housed separately.
- Comprehensiveness of Collection: No library can hope to maintain comprehensiveness, that is, the most extensive and intensive collection, in all fields or subjects is practicable.
- Subject Coverage: Subject coverage will depend upon the size and the social and economic background of the population served by the authority. It means to select preferable element from a number of titles published in a subject, when the library ought to cover.
- Balanced Collection: A balanced collection of a library is not a matter merely of a wide of subject matter but also all topics without any biases and emotional matter of librarian. He should be able through advice and guidance to establish his own particular balance.
It is apparent that the size, nature and contents of the library collection depend upon the objectives of the library and the needs of the clientele. A live, balanced and up-to-date collection should be maintained both in subject content and in kinds of materials. The library being a growing organism should be continuous in addition of new materials.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College