Conceptual Framework of Customer Satisfaction:
Customer satisfaction is not just a buzzword in the business world; it’s a crucial component of any successful business strategy. It is defined as an overall evaluation based on the total purchase and consumption experience with a product or service over time (Fornell et al., 1996). Understanding the dynamics of customer satisfaction is essential for predicting and shaping future customer behavior. In the rest of this article, we will explore the conceptual framework of customer satisfaction.
Section 1: Defining Customer Satisfaction: A Pleasurable Fulfillment
Customer satisfaction is a multifaceted concept that plays a pivotal role in the realm of business and marketing. Richard (1999) provides a concise yet profound definition of customer satisfaction as a “pleasurable fulfillment.” This definition encapsulates the essence of customer satisfaction, which extends far beyond a simple transaction or a one-time interaction. It encompasses the entire spectrum of emotions and experiences that a customer encounters during their interaction with a product or service. To break down this definition further:
- Pleasurable Fulfillment: Satisfaction is fundamentally linked to the emotional state of the customer. When a customer experiences pleasurable fulfillment, it means that their interaction with a product or service has provided them with a sense of contentment, happiness, and fulfillment. This emotional connection is a key component of customer satisfaction.
- Consumer’s Needs, Desires, and Goals: Satisfaction is intricately tied to the fulfillment of the customer’s needs, desires, and goals. It’s not solely about the utility of a product or service but also about how well it aligns with the customer’s specific requirements. A product or service that helps a customer achieve their goals or fulfill their desires contributes significantly to their satisfaction.
- Sense of Delight and Pleasure: Customer satisfaction goes beyond mere utility. It involves the creation of delight and pleasure in the customer’s experience. This goes beyond meeting basic needs and extends into the realm of emotional and psychological fulfillment. When a customer feels delighted and pleased with their experience, it is a testament to the organization’s ability to deliver satisfaction.
Customer Satisfaction as a Barometer: Customer satisfaction serves as a critical barometer for an organization. It provides insights into how well a company is meeting its customers’ needs and expectations. Hill et al. (2007) highlight that it acts as a predictive tool for future customer behavior. This means that the level of customer satisfaction is a strong indicator of how customers are likely to engage with the company in the future.
When customers are highly satisfied, they are more likely to continue doing business with the organization. They become repeat customers and advocates for the brand, which, in turn, can drive profitability and growth. On the other hand, when customers are dissatisfied, they are more likely to disengage from the company, seek alternatives, or share their negative experiences, which can have a detrimental impact on the organization.
The comparison between the outcomes of a product or service and the customer’s set of expectations is a central element in understanding customer satisfaction. When the customer’s experience matches or exceeds their initial expectations, satisfaction tends to increase. Conversely, when the customer’s experience falls short of their expectations, it can lead to dissatisfaction.
In brief, customer satisfaction, as described by Richard (1999), is a state of pleasurable fulfillment that results from the alignment of a product or service with a customer’s needs, desires, and goals. It encompasses the creation of delight and pleasure in the customer’s experience. Moreover, customer satisfaction acts as a barometer for an organization, offering insights into future customer behavior based on their level of satisfaction and the alignment of their experiences with their expectations. Understanding and managing customer satisfaction is essential for building long-term customer relationships and achieving success in today’s competitive marketplace.
Section 2: Positive Consequences of Customer Satisfaction: A Catalyst for Success
Customer satisfaction is not just a feel-good metric; it has tangible and far-reaching positive consequences that significantly impact an organization’s performance and bottom line. Let’s delve into two crucial dimensions:
2.1 Impact on Market Share and Brand Equity: Customer satisfaction serves as a linchpin in a business’s quest for market share and the establishment of brand equity. Pappu & Quester (2006) underscore the direct link between customer satisfaction and these key outcomes.
- Market Share: In a competitive marketplace, the ability to capture and retain a share of the market is essential. Satisfied customers are not just one-time buyers; they are more likely to be loyal customers who return for repeat purchases. Their loyalty translates into higher customer retention rates and a more significant market share for the organization. Satisfied customers act as brand advocates, spreading positive word-of-mouth recommendations, which, in turn, can attract new customers and contribute to an expanded market share.
- Brand Equity: Brand equity is an intangible yet invaluable asset for a business. It encompasses the reputation, trust, and perceived value that customers associate with a brand. Customer satisfaction plays a pivotal role in building and strengthening brand equity. When customers consistently experience satisfaction with a brand, it enhances their perception of the brand’s value. This positive association elevates the brand’s equity and positions it favorably in the minds of consumers. Strong brand equity, in turn, can lead to premium pricing, customer loyalty, and a competitive advantage in the market.
2.2 Impact on Organizational Revenue: One of the most direct and quantifiable consequences of customer satisfaction is its influence on organizational revenue, as highlighted by Assaf et al. (2012).
- Increased Revenue: Higher levels of customer satisfaction often translate into increased sales and revenue for organizations. Satisfied customers are not only more likely to return for repeat purchases, but they are also more likely to engage in cross-selling or upselling opportunities. They trust the brand and are open to exploring new products or services offered by the organization. This can significantly boost the top-line revenue figures.
- Reduced Customer Churn: Customer satisfaction also plays a critical role in reducing customer churn or attrition. Satisfied customers are less likely to defect to competitors or seek alternatives. Their loyalty serves as a protective shield against revenue loss. Organizations with a satisfied customer base can focus on retaining these customers, which is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Reduced churn contributes to sustainable revenue streams.
Customer satisfaction is a catalyst for success in today’s business landscape. It not only impacts market share and strengthens brand equity but also has a direct influence on organizational revenue. Satisfied customers are not only more loyal but also more likely to generate positive word-of-mouth, attracting new customers and expanding the market share. Their trust and loyalty lead to increased sales, reduced churn, and ultimately contribute to the financial health and sustainability of the organization. As such, understanding and actively managing customer satisfaction is a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in a competitive environment.
Section 3: Factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction: The Building Blocks of Contentment
Customer satisfaction is a multifaceted outcome that is shaped by a range of interrelated factors. Organizations that understand and address these factors are better positioned to create satisfied customers. Here are some key factors that influence customer satisfaction:
3.1 Product Features and Quality: The features and quality of a product or service are fundamental determinants of customer satisfaction. Customers expect products to meet or exceed certain standards and to perform the functions they were designed for. If the features are aligned with customer needs and desires, and the quality is high, customers are more likely to be satisfied.
3.2 Reliability: Reliability is another essential factor. Customers want products or services that consistently perform as expected. When customers can rely on a product to function as promised without unexpected breakdowns or issues, it enhances their satisfaction. Reliability instills trust in the brand.
3.3 Sales Activities: The sales process is often the first point of contact between a customer and an organization. The professionalism and effectiveness of sales activities significantly influence customer satisfaction. This includes the ease of purchasing, the competence of sales representatives, and the transparency of pricing and terms.
3.4 Customer Support: Customer support plays a pivotal role in post-purchase satisfaction. When customers encounter issues or have questions, prompt and effective customer support can make a substantial difference. Supportive and responsive customer service representatives can turn a potentially negative experience into a positive one, enhancing overall satisfaction.
3.5 Meeting or Exceeding Expectations: Meeting or exceeding customer expectations is at the heart of customer satisfaction. When the actual experience aligns with or surpasses the expectations that customers had before the purchase, it leads to satisfaction. Organizations that set clear, realistic expectations and then consistently deliver on those expectations are more likely to create satisfied customers.
3.6 Role of Satisfied Customers as Brand Advocates: Satisfied customers are not just passive recipients of good service; they often become active brand advocates. When customers have positive experiences with a brand, they are more likely to share these experiences with their social networks, friends, and family. These positive word-of-mouth recommendations can have a powerful effect.
Satisfied customers effectively become brand ambassadors, influencing the purchasing decisions of others. Their advocacy can attract new potential customers, essentially serving as an extension of the organization’s marketing efforts. This word-of-mouth marketing is highly effective because it comes from a trusted source—someone who has experienced and enjoyed the brand’s products or services.
Customer satisfaction is a result of several factors working in harmony. Product features, quality, reliability, sales activities, and customer support all play a crucial role in shaping the customer’s experience. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations is central to satisfaction, and organizations that prioritize this are more likely to create satisfied customers.
Moreover, satisfied customers often become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences and acting as a powerful force for attracting new customers. In a world where customer reviews and recommendations carry significant weight, harnessing the advocacy of satisfied customers is a strategic advantage for any organization seeking to build its reputation and customer base.
Section 4: The Crucial Role of a “Customer-Centric” Approach in Customer Satisfaction and Retention:
A “customer-centric” approach is not just a business strategy; it’s a philosophy that places the customer at the epicenter of all organizational activities. This approach, rooted in customer-centricity, is paramount for several reasons, particularly in the context of improving customer satisfaction and retaining customers.
4.1 Meeting Customer Needs and Desires: A “customer-centric” approach commences with an in-depth understanding of customer needs and desires. By actively engaging with customers and listening to their feedback, organizations gain valuable insights into what matters most to their customer base. This knowledge becomes the foundation for tailoring products, services, and processes to meet, and ideally exceed, customer expectations. When customers recognize that an organization understands and caters to their unique needs, their satisfaction levels rise significantly.
4.2 Enhancing the Customer Experience: Customer satisfaction is intrinsically linked to the customer experience. A “customer-centric” approach prioritizes the entire customer journey, from initial interactions to post-purchase support. Ensuring a seamless, user-friendly, and positive experience at every touchpoint is a cornerstone of elevating customer satisfaction. Whether through intuitive website design, efficient customer service, or personalized recommendations, every facet of the customer experience plays a pivotal role in satisfaction.
4.3 Building Trust and Loyalty: Trust is the bedrock of enduring customer relationships. By consistently delivering on promises and surpassing customer expectations, organizations can nurture trust with their customers. This trust, in turn, breeds loyalty. Satisfied customers, who trust a brand, are more likely to return for repeat purchases and continue their affiliation with the company. They transition from mere customers to advocates, influencing others and contributing to positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
4.4 Competitive Advantage: In a marketplace inundated with alternatives, a “customer-centric” approach can set an organization apart from the competition. When competitors offer similar products or services, the manner in which an organization treats its customers emerges as a critical differentiator. Providing exceptional customer service and consistently meeting or surpassing customer expectations can furnish an organization with a compelling competitive edge.
4.5 Addressing Service Quality, Product Quality, and Value for Money: Service quality, product quality, and value for money are paramount to customer satisfaction. Customers expect services and products that align with their requirements, offer high quality, and provide value commensurate with the price paid. Organizations that focus on delivering on these three fronts directly contribute to customer satisfaction.
4.6 In the Face of Competition: Customer-centricity is not only about satisfying customers but also retaining them. In a competitive landscape, where rivals are actively working to enhance customer satisfaction, organizations that don’t prioritize customer-centricity risk losing their customer base. To mitigate the potential for customer churn, organizations must place a strong emphasis on the quality of service, product, and value they provide.
A “customer-centric” approach is indispensable for improving customer satisfaction and retaining customers. It revolves around understanding and meeting customer needs, delivering outstanding customer experiences, fostering trust, gaining a competitive edge, and safeguarding against customer churn in the face of competition.
Moreover, it entails a focus on service quality, product quality, and value for money. In a world where customer expectations are constantly evolving, organizations that embrace customer-centricity are better positioned to succeed, grow, and thrive. In essence, customer satisfaction is not merely a transactional objective; it’s a strategic pursuit that necessitates a customer-centric approach to offer value and nurture enduring customer relationships.
Section 5: Importance of Employee Satisfaction: Fueling Customer Satisfaction
Employee satisfaction is not an isolated aspect within an organization; it’s intricately linked to customer satisfaction and the overall success of a business. Here’s a brief look at why employee satisfaction is paramount:
5.1 The Employee-Customer Link: Employees are the bridge between an organization and its customers. They are the ones who interact directly with customers, whether it’s in a retail store, through customer service calls, or during face-to-face meetings. Their attitude, behavior, and level of satisfaction significantly influence how customers perceive and interact with the organization.
5.2 Service Quality and Customer Experience: Satisfied employees are more likely to be motivated, engaged, and committed to their work. When employees are content and motivated, they are more inclined to provide high-quality service to customers. This, in turn, enhances the overall customer experience. Satisfied employees tend to go the extra mile, demonstrating better interpersonal skills, problem-solving abilities, and a genuine desire to meet customer needs.
5.3 Reducing Employee Turnover: High employee turnover can be detrimental to an organization. It disrupts operations, requires additional resources for recruitment and training, and can negatively impact the consistency of customer service. Satisfied employees are more likely to stay with their current employer, reducing the costs and challenges associated with high turnover rates. Retaining experienced and well-trained employees is beneficial for maintaining consistent customer service standards.
5.4 Employee Engagement and Commitment: Employee satisfaction fosters higher levels of engagement and commitment. Engaged employees are passionate about their work, and they take pride in delivering quality service. Their enthusiasm is contagious and can influence the positive atmosphere in the workplace, ultimately benefiting customer interactions.
5.5 Brand Advocacy: Satisfied employees are more likely to be brand advocates. They believe in the organization’s values and mission, which they can effectively convey to customers. Their advocacy creates a positive image of the organization, and customers are more likely to trust and engage with a brand that has passionate and satisfied employees.
5.6 Internal Customer Satisfaction: Internal customers, or employees, play a vital role in ensuring customer satisfaction. When employees themselves are satisfied with their work environment, they are more likely to collaborate effectively, communicate better, and coordinate their efforts to meet customer needs. This internal cohesion has a direct impact on external customer satisfaction.
5.7 Employee Feedback and Innovation: Satisfied employees are more likely to provide constructive feedback and contribute to innovation within the organization. They understand the customer’s perspective and can offer valuable insights to improve products, services, and processes, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction.
5.8 Overall Organizational Performance: Employee satisfaction is closely tied to overall organizational performance. When employees are satisfied, they are more productive, dedicated, and aligned with the company’s goals. This holistic improvement in organizational performance ultimately benefits customer satisfaction, as it leads to better products, services, and customer interactions.
Employee satisfaction is a critical element that significantly impacts customer satisfaction. Satisfied employees are more likely to provide high-quality service, engage with customers effectively, and contribute to a positive workplace culture. Their commitment and advocacy create a virtuous cycle, where customer satisfaction is enhanced, leading to customer loyalty and business success. Recognizing the interdependence of employee and customer satisfaction is essential for organizations that aim to thrive and build long-term, meaningful customer relationships.
Section 6: The Dynamic Nature of Customer Satisfaction: Understanding the Complex Journey
Customer satisfaction is not a static or one-time event; rather, it’s a dynamic process influenced by numerous factors. Understanding this dynamism is crucial for organizations seeking to maintain and enhance customer satisfaction. Here’s a look at the dynamic nature of customer satisfaction:
6.1 Timing and Experience: Timing of Product Usage or Service Experiences: Customer satisfaction can fluctuate over time due to the timing of product usage or service experiences. For example, a customer’s satisfaction may vary depending on when they encounter a product or service. An initial positive experience may lead to high satisfaction, but if subsequent experiences do not meet expectations, satisfaction can decline. Conversely, a series of consistently positive experiences can elevate satisfaction levels over time.
6.2 Factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction:
- Quality: The quality of a product or service is a primary driver of customer satisfaction. Customers expect products and services to meet or exceed certain standards. Variations in quality can directly impact satisfaction levels. Consistently high-quality offerings lead to higher satisfaction.
- Emotional Responses: Customer satisfaction is not solely rational; emotions play a significant role. Positive emotional responses, such as joy, excitement, or delight, can enhance satisfaction. Conversely, negative emotions, like frustration or disappointment, can reduce satisfaction levels. Understanding and managing the emotional aspect of customer experiences is crucial.
- Attribution: Attribution refers to how customers attribute the causes of their experiences. When customers attribute their positive experiences to an organization’s efforts, it boosts satisfaction. However, if they attribute negative experiences to the organization, it can lead to dissatisfaction. Managing customer attribution is essential for shaping satisfaction.
- Perceptions About Equity: Customers often assess the fairness and equity of their interactions with a company. If they perceive that they are treated fairly, they are more likely to be satisfied. Conversely, perceptions of unfairness or unequal treatment can diminish satisfaction. Organizations need to ensure fairness in their dealings with customers to maintain satisfaction levels.
6.3 Customer Expectations: Customer expectations are a fundamental factor in the dynamic nature of satisfaction. Customer satisfaction is often measured as the gap between customer expectations and their actual experiences. If expectations change over time, satisfaction can evolve accordingly. Managing and aligning customer expectations is essential to prevent satisfaction fluctuations.
6.4 The Cumulative Effect: Customer satisfaction is often influenced by the cumulative effect of multiple interactions and experiences with a brand. Positive experiences, when repeated or consistently provided, lead to high overall satisfaction. Conversely, a series of negative experiences can significantly erode satisfaction.
6.5 Customer Feedback and Adaptation: Organizations that actively seek and respond to customer feedback are better equipped to adapt and evolve their products, services, and processes. Customer feedback serves as a dynamic source of information that can guide improvements and influence satisfaction levels positively.
Customer satisfaction is a dynamic, evolving process influenced by various factors. Timing of product usage or service experiences, the quality of offerings, emotional responses, attribution, and perceptions about equity are just a few of the elements that can impact customer satisfaction. Organizations that understand the dynamic nature of satisfaction and actively manage these factors are better positioned to maintain and enhance satisfaction over time. A customer-centric approach that considers not only what satisfies customers today but also what will satisfy them in the future is essential for long-term success in today’s ever-changing business landscape.
Section 7: Customer Loyalty: The Ultimate Goal of Customer Satisfaction
Customer loyalty is the coveted pinnacle that every business aspires to reach. It represents a state where customers not only return for repeat purchases but also become steadfast advocates for a brand. Here’s an exploration of the link between customer satisfaction and loyalty:
7.1 Understanding Customer Loyalty: Customer loyalty is the culmination of a positive and enduring relationship between a customer and a brand. It goes beyond mere transactional interactions; it embodies a sense of commitment, trust, and allegiance that customers feel toward a particular brand or company.
7.2 The Role of Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction is the precursor to customer loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to transition into loyal customers. When customers experience satisfaction in their initial interactions with a brand, it establishes the foundation of trust and goodwill. These satisfied customers are then more inclined to return for repeat purchases.
7.3 Extending the Customer Lifecycle: Customer loyalty is characterized by the extension of the customer lifecycle. Loyal customers continue their association with a brand for an extended period, making repeated purchases and thus contributing to the long-term revenue of the organization. In contrast to one-time buyers, loyal customers represent a sustainable revenue stream.
7.4 Positive Word-of-Mouth Recommendations: Loyal customers are not just silent admirers of a brand; they are often vocal advocates. They willingly share their positive experiences with friends, family, and colleagues. This positive word-of-mouth recommendation can significantly impact the acquisition of new customers. Recommendations from existing loyal customers carry a high level of trust and credibility.
7.5 Repeat Purchases and Cross-Selling: Satisfied customers who transition into loyal customers are more likely to make repeat purchases. They have trust in the brand, are familiar with its offerings, and appreciate the value it provides. Additionally, they are open to exploring new products or services offered by the brand, making them ideal candidates for cross-selling and upselling.
7.6 Factors Shaping Loyalty: Customer loyalty is not solely based on the satisfaction of a single transaction. It is a cumulative outcome influenced by a series of satisfying experiences. Factors that contribute to loyalty include consistent quality, personalized interactions, trust, reliability, and positive emotional connections with the brand.
7.7 Challenges in Building Loyalty: Building customer loyalty is not without challenges. It requires sustained effort to maintain customer satisfaction and reinforce positive experiences. Organizations must continually adapt to changing customer needs, expectations, and market dynamics to ensure ongoing loyalty.
7.8 The Competitive Advantage of Loyalty: Customer loyalty provides organizations with a significant competitive advantage. Loyal customers are less likely to be swayed by competitors offering similar products or services. They tend to stick with the brand they trust, even when faced with alternatives.
Customer satisfaction is the Launchpad for customer loyalty. It’s the initial stage where trust and goodwill are established. Loyal customers, nurtured through consistent satisfaction, extend the customer lifecycle, generate positive word-of-mouth recommendations, and contribute to long-term revenue. Building customer loyalty is an ongoing effort that requires the delivery of high-quality products and services, personalized interactions, and a commitment to exceeding customer expectations. In today’s competitive business landscape, customer loyalty is a key differentiator and a source of sustainable growth.
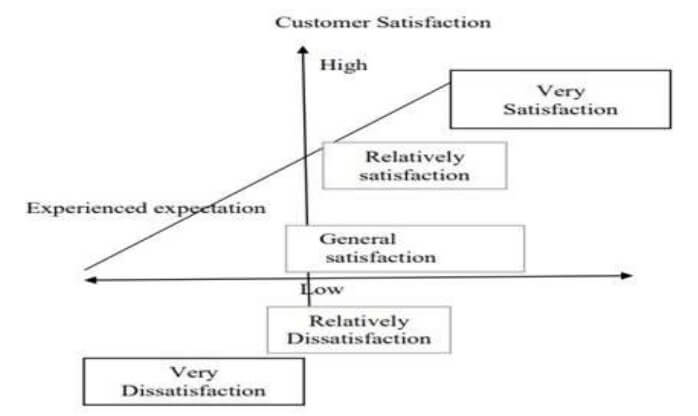
Section 8: Customer Satisfaction Analysis Model: A Closer Look
The Customer Satisfaction Analysis Model is a framework that helps organizations understand and measure customer satisfaction by examining the interplay between customer expectations and their actual experiences. Here’s an exploration of this model:
8.1 Customer Expectations vs. Actual Experiences: At the core of this model is the concept that customer satisfaction is determined by the alignment or disalignment between customer expectations and their actual experiences. Customer expectations encompass what customers anticipate from a product, service, or brand, while actual experiences pertain to the real encounters they have with these offerings.
8.2 The Five Intervals: The model categorizes the relationship between customer expectations and actual experiences into five distinct intervals:
- Very Dissatisfied: In this scenario, customer expectations are significantly higher than the actual experiences. Customers experience severe disappointment, and their satisfaction levels plummet. These customers are likely to share negative feedback and may cease further interactions with the brand.
- Relatively Dissatisfied: Here, customer expectations are higher than their actual experiences, but the disparity is not as extreme as in the “very dissatisfied” category. While not in the realm of severe dissatisfaction, these customers are still discontented and may be at risk of churning.
- General Satisfaction: General satisfaction is characterized by a balance between customer expectations and their actual experiences. In this interval, customers find that their experiences meet their expectations reasonably well. They are content but may not exhibit strong loyalty or advocacy.
- Relatively Satisfied: Customer expectations are exceeded by their actual experiences in this category. These customers are pleasantly surprised by the value they receive, which leads to a higher level of satisfaction. They are more likely to continue patronizing the brand and may share positive feedback.
- Very Satisfied: The pinnacle of customer satisfaction, “very satisfied” customers find that their actual experiences far surpass their expectations. These customers are not only loyal but also enthusiastic advocates for the brand. They are likely to engage in repeat business and provide strong positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
8.3 Implications for Organizations: Understanding where customers fall within these five intervals is essential for organizations. It provides insights into areas for improvement, whether it’s aligning customer expectations with actual experiences or exceeding expectations to achieve higher levels of satisfaction.
Organizations must actively gather customer feedback, analyze their expectations, and measure their satisfaction levels to assess where they fall within these intervals. This information guides strategic decision-making to enhance customer satisfaction.
8.4 Managing Expectations and Experiences: To move customers from the lower intervals (dissatisfied) to the higher intervals (satisfied), organizations must actively manage both customer expectations and experiences. This involves setting clear expectations through marketing, sales, and customer communication, and then consistently delivering experiences that meet or exceed those expectations.
8.5 The Continuous Cycle: The model underscores that customer satisfaction is a continuous cycle. As customer expectations evolve, organizations must adapt to meet these changing demands. Additionally, feedback from customers in different intervals can inform organizations about their performance and help them make necessary adjustments.
The Customer Satisfaction Analysis Model provides a structured framework for understanding customer satisfaction based on the relationship between customer expectations and actual experiences. The five intervals, ranging from very dissatisfied to very satisfied, offer a roadmap for organizations to assess and enhance customer satisfaction, ultimately driving customer loyalty and advocacy. Customer satisfaction is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process that requires ongoing attention and responsiveness to customer needs and expectations.
Section 9: Improving Customer Satisfaction: Two Key Approaches
Enhancing customer satisfaction is a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to build lasting customer relationships and secure a competitive advantage. Two primary approaches are employed to achieve this goal:
- Service Improvement:
9.1.1 Enhancing the Customer Experience: Service improvement focuses on optimizing every aspect of the customer experience. This approach entails making changes and refinements in various areas to ensure that customers have a positive, memorable interaction with the brand.
9.1.2 Key Aspects of Service Improvement:
- Quality Assurance: Maintaining consistent quality is fundamental. Organizations must strive to deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. This requires rigorous quality control processes and a commitment to continuous improvement.
- Efficient Processes: Streamlining internal processes, such as order fulfillment, customer support, and delivery, can reduce customer wait times and improve efficiency. This leads to faster and more satisfying experiences.
- Personalization: Tailoring interactions to meet individual customer needs and preferences can significantly enhance satisfaction. Personalization can range from recommending products based on past purchases to addressing customers by their names.
- Proactive Problem Resolution: Addressing issues before they escalate is key. A proactive approach to resolving customer concerns demonstrates a commitment to their well-being and can transform potentially negative experiences into positive ones.
- Communication: Effective communication is essential. Keeping customers informed about order status, expected delivery times, and any changes in services or products can eliminate surprises and promote satisfaction.
- Employee Training: Well-trained employees are better equipped to deliver exceptional service. Investing in employee training ensures that staff can respond to customer inquiries and solve problems effectively.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Gathering feedback from customers is crucial for identifying areas that require improvement. Organizations should have mechanisms in place, such as surveys and reviews, to collect customer insights.
9.2 Managing Customer Expectations:
9.2.1 Reducing the Desired Level of Expectations: Managing customer expectations is another critical approach to enhancing satisfaction. It involves setting and aligning customer expectations with what the organization can realistically deliver. This can help prevent situations where customer expectations are unattainably high, leading to potential dissatisfaction.
9.2.2 Key Aspects of Managing Customer Expectations:
- Transparency: Organizations should be transparent about their offerings, pricing, and service levels. This transparency helps customers make informed decisions and prevents unwarranted surprises.
- Clear Communication: Clearly communicating what customers can expect regarding product or service features, delivery times, and support is essential. This ensures that customers have a realistic understanding of what they are purchasing.
- Underpromising and Overdelivering: Underpromising is about setting conservative expectations. This gives organizations the opportunity to exceed those expectations. When customers receive more than they anticipated, it fosters a positive perception.
- Realistic Timeframes: Setting realistic timeframes for product or service delivery is vital. Overpromising on delivery times can lead to customer dissatisfaction, while realistic estimates promote a smoother experience.
- Educating Customers: Providing customers with clear and accurate information about product usage, benefits, and potential limitations can manage their expectations effectively.
- Managing Peak Demand: During peak demand periods, managing expectations becomes particularly important. Organizations should clearly communicate potential delays or limitations during high-traffic periods.
9.3 Balancing Both Approaches: The most effective approach to improving customer satisfaction often involves a combination of service improvement and managing customer expectations. By delivering high-quality service and ensuring that customer expectations are realistic, organizations can consistently meet or exceed customer satisfaction levels.
9.4 Continuous Improvement: Improving customer satisfaction is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment. Organizations should continuously assess and enhance their services and manage customer expectations as both evolve over time.
Organizations can significantly enhance customer satisfaction by focusing on service improvement and effectively managing customer expectations. These complementary approaches ensure that customers receive consistent, high-quality experiences and are well-informed about what they can expect. A customer-centric commitment to continuous improvement is essential for building lasting customer relationships and sustaining long-term success.
Section 10: The Ultimate Goal: Customer Satisfaction and its Role in Success
Customer satisfaction is the lynchpin of success for any organization. It is the ultimate outcome of comparing customer expectations with their actual experiences. When a company can consistently meet or exceed these expectations, customer satisfaction thrives. Here’s a closer look at the role of customer satisfaction and its connection to customer loyalty:
10.1 The Foundation of Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction is the result of customers receiving an experience that aligns with or surpasses their expectations. When customers engage with a brand and find that their interactions consistently meet or exceed their expectations, they experience satisfaction.
10.2 The Dynamics of Customer Loyalty: Customer loyalty is not an isolated concept; it’s intrinsically linked to customer satisfaction. In essence, customer satisfaction is the precursor to customer loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to transition into loyal customers. Their satisfaction with previous experiences establishes the foundation of trust and goodwill that is essential for building loyalty.
10.3 Key Elements in Determining Success: Customer satisfaction and loyalty are pivotal determinants of success in the market. Here’s how these elements contribute to organizational success:
- Market Share: Satisfied and loyal customers are more likely to stay with a brand and continue making repeat purchases. This not only solidifies the brand’s market share but also reduces the churn rate. A higher market share means a more significant presence in the market.
- Profitability: Loyal customers contribute significantly to an organization’s profitability. They not only generate repeat business but also tend to make larger and more frequent purchases. This consistent revenue stream boosts profitability.
- Brand Equity: Customer satisfaction and loyalty are key drivers of brand equity. Positive customer experiences and advocacy from loyal customers enhance the brand’s reputation and equity. This, in turn, attracts new customers and contributes to long-term success.
- Word-of-Mouth Recommendations: Satisfied and loyal customers are more likely to provide positive word-of-mouth recommendations. Their advocacy acts as a powerful marketing tool, influencing others to engage with the brand. These recommendations are often trusted and can bring in new customers.
- Extended Customer Lifecycle: Loyal customers extend the customer lifecycle for an organization. Their continued engagement ensures a sustainable relationship, which is more cost-effective than acquiring new customers.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Loyal customers are not only open to repeat purchases but also to exploring additional offerings from the brand. This presents opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, further contributing to success.
10.4 Continuous Effort and Commitment: Achieving and maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty require continuous effort and commitment. Organizations must consistently deliver high-quality products and services, personalize interactions, and exceed customer expectations.
10.5 Customer-Centric Culture: A customer-centric culture is crucial for fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty. It involves placing the customer at the center of all organizational efforts, from product development to customer support. This culture ensures that the organization is continually focused on meeting and exceeding customer needs and expectations.
Customer satisfaction is the ultimate goal for organizations. It stems from delivering experiences that match or surpass customer expectations. This satisfaction is the foundation upon which customer loyalty is built, and both elements are vital for organizational success. High levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty contribute to market share, profitability, brand equity, and positive word-of-mouth recommendations. Building a customer-centric culture and sustaining efforts to meet evolving customer expectations are essential for long-term success in today’s competitive market.
In conclusion, understanding customer satisfaction is not just about meeting expectations; it’s about exceeding them. Satisfied customers become loyal advocates, contributing to a company’s success and profitability. By continuously monitoring and improving customer satisfaction, businesses can build strong customer relationships, enhance brand equity, and stay ahead in the competitive market.
References:
- Assaf, A. G., & Magnini, V. (2012). Accounting for customer satisfaction in measuring hotel efficiency: Evidence from the US hotel industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(3), 642–647.
- Barnes, J. G. (2006). Building your customer strategy: A guide to creating profitable customer relationships. John Wiley & Sons.
- Basavaraj, Mr, Sulibhavi, & Ka, S. (2017). Brand image and trust on customers’ loyalty: A study on private label brands in Hubli-Dharwad conglomerate city of Karnataka.
- Fornell, C., Johnson, M. D., Anderson, E. W., Cha, J., & Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American customer satisfaction index: Nature, purpose and findings. Journal of Marketing, 60(4), 7–18.
- Jajoo, S. (2023). Customer Satisfaction, Customer Delight, and Customer Ecstasy as Antecedents of Brand Loyalty in Online Shopping (Doctoral dissertation). Shri Vaishnav School of Management, Created and maintained by INFLIBNET Centre. http://hdl.handle.net/10603/520773.
- Jiradilok, T., Malisuwan, S., Madan, N., & Sivaraks, J. (2014). The impact of customer satisfaction on online purchasing: A case study analysis in Thailand. Journal of Economics, Business and Management, 2, 5–11.
- Khedkar, E. B. (2015). Effect of customer relationship management on customer satisfaction and loyalty. International Journal of Management, 6(5), 01–07.
- Kiel, G. C., & Layton, R. A. (1981). Dimensions of consumer information seeking behavior. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(2), 233–23.
- McDonald, M., & Keen, P. (2000). The eProcess Edge: Creating customer value and business in the internet era. The McGraw-Hill Companies.
- Swain, B. K. (2013). Measuring customer services through Customer Satisfaction Index.
- Szymanski, D. M., & Hise, R. T. (2000). E-satisfaction: An initial examination. Journal of Retailing, 76(3), 309–322.
- Tandon, U., & Ertz, M. (2021). Customer satisfaction towards online shopping by empirical validation of Self-Determination Theory. In Handbook of research on the platform economy and the evolution of e-commerce (pp. 177–203).
- Tandon, U., Kiran, R., & Sah, A. (2017). Analyzing customer satisfaction: Users’ perspective towards online shopping. Nankai Business Review International, 8(3), 266–288.
- Tao, F. F. (2014). Customer relationship management based on increasing customer satisfaction. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 5, 256–263.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College