Curriculum Design in Physical Education:
Curriculum design in Physical Education (PE) is a complex and dynamic process aimed at shaping the physical, mental, and social development of students. PE programs go beyond mere physical activity; they are carefully constructed to provide a structured and comprehensive educational experience. This article delves into curriculum design in physical education.
Importance of Curriculum Design in Physical Education:
The importance of curriculum design in Physical Education (PE) cannot be overstated, as it plays a pivotal role in shaping the educational experience and outcomes of students. Here are some key reasons highlighting the significance of curriculum design in PE:
1. Educational Framework: Curriculum design provides a structured framework for delivering educational content and experiences in PE. It outlines the objectives, content, and assessment methods, ensuring that the educational goals are clearly defined and attainable (SHAPE America, 2014).
2. Clear Learning Objectives: A well-designed curriculum sets clear and measurable learning objectives. In PE, these objectives encompass physical fitness, motor skill development, sportsmanship, teamwork, and health education. These objectives guide instructors in planning lessons that align with educational outcomes (NASPE, 2009).
3. Comprehensive Development: PE curriculum design considers not only physical development but also cognitive, emotional, and social development. It promotes critical thinking, decision-making, problem-solving, self-confidence, resilience, and interpersonal skills (NAPES, 2020).
4. Inclusivity: A thoughtfully designed curriculum ensures inclusivity by accommodating the diverse needs of all students, including those with disabilities or different skill levels. Adaptations and modifications are integrated to create an environment where every student can participate and succeed (Inclusive Fitness Coalition, 2021).
5. Promoting Lifelong Physical Activity: The curriculum introduces students to a variety of physical activities and educates them about the benefits of an active lifestyle. By fostering a love for physical activity and imparting the knowledge and skills needed for lifelong engagement, the PE curriculum contributes to long-term health and well-being (SHAPE America, 2014).
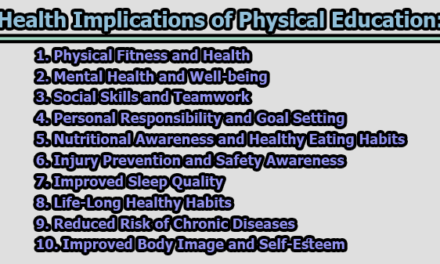
6. Health Education: Incorporating health education into the curriculum empowers students to make informed decisions about their health. They learn about the importance of physical activity, nutrition, and the risks associated with unhealthy behaviors. This knowledge equips them to lead healthier lives and make choices that reduce the risk of chronic diseases (CDC, 2020).
7. Assessment and Improvement: Curriculum design includes assessment and evaluation methods to measure student progress and the achievement of learning objectives. Regular assessment allows instructors to adapt the curriculum to meet individual student needs and make continuous improvements (CDC, 2019).
8. Alignment with Educational Goals: A well-designed PE curriculum aligns with the broader educational goals of the institution. It enhances academic achievement by promoting cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making. This alignment contributes to the overall educational success of students (NASPE, 2009).
9. Life Skills: PE curriculum design emphasizes the development of life skills that extend beyond the gymnasium. These skills include teamwork, leadership, communication, and conflict resolution, which are transferable to various aspects of life, including academic and professional pursuits (NAPES, 2020).
10. Holistic Development: Curriculum design in PE aims to nurture well-rounded individuals by addressing physical, mental, emotional, and social aspects of development. It fosters a comprehensive approach to education that prepares students for success in multiple dimensions of life (SHAPE America, 2014).
Key Components of Curriculum Design in Physical Education:
The curriculum design in Physical Education (PE) involves several key components that are essential for creating a well-structured and effective educational program. These components ensure that the curriculum aligns with educational objectives, fosters student development, and provides a comprehensive learning experience. Here are the key components of curriculum design in PE:
1. Learning Objectives: Learning objectives serve as the foundation of curriculum design in PE. These objectives define what students are expected to achieve by the end of the program. They typically include physical fitness goals, motor skill development, sportsmanship, teamwork, and health education outcomes. Clear and measurable objectives guide instructors in planning lessons and assessing student progress (SHAPE America, 2014).
2. Content and Activities: Curriculum design includes the selection of appropriate content and activities that align with the defined learning objectives. This component encompasses a wide range of physical activities, such as sports, dance, fitness routines, and recreational games. A well-rounded curriculum exposes students to various physical activities, allowing them to explore their interests and develop proficiency in different skills (NASPE, 2009).
3. Assessment and Evaluation: Effective assessment and evaluation methods are integral components of curriculum design. Assessment tools, such as fitness tests, skill assessments, and self-reflection exercises, are used to measure student progress and their achievement of learning objectives. Continuous evaluation allows instructors to track individual student development and adapt the curriculum accordingly (CDC, 2019).
4. Inclusivity and Adaptation: An inclusive curriculum design ensures that students of all abilities and backgrounds can participate. This component involves making adaptations and modifications to accommodate diverse needs. Inclusivity measures create an environment where every student has the opportunity to engage and succeed in physical activities (Inclusive Fitness Coalition, 2021).
5. Health Education Integration: Integrating health education into the curriculum is crucial. This component involves teaching students about the benefits of physical activity, healthy eating habits, and the risks associated with unhealthy behaviors. Health education equips students with the knowledge and skills needed to make informed decisions about their health and well-being (CDC, 2020).
6. Sequence and Progression: Curriculum design in PE should consider the logical sequence and progression of content and activities. Activities should be organized in a way that allows students to build upon their skills and knowledge incrementally. A structured sequence ensures that students develop a solid foundation before advancing to more complex activities (NASPE, 2009).
7. Resources and Materials: Identifying the necessary resources and materials is an essential component. This includes equipment, facilities, textbooks, online resources, and any other materials required for effective instruction. Availability and access to these resources impact the implementation of the curriculum (SHAPE America, 2014).
8. Teacher Training and Professional Development: Ensuring that instructors are adequately trained and receive ongoing professional development is crucial. Teachers should be well-versed in the curriculum, assessment methods, and instructional strategies. Ongoing training helps instructors stay current with best practices in PE education (NASPE, 2009).
9. Alignment with Educational Goals: The curriculum should align with the broader educational goals of the institution or school district. This ensures that PE education complements and supports the overall educational mission. Alignment with educational goals contributes to the academic success and well-rounded development of students (NAPES, 2020).
10. Flexibility and Adaptability: Curriculum design should allow for flexibility and adaptability. It should accommodate changes in student demographics, emerging trends in physical activity, and evolving educational standards. A curriculum that can adapt to new challenges and opportunities remains relevant over time (CDC, 2019).
Role of Curriculum Design in Fostering Active, Healthy, and Educated Individuals:
A well-designed PE curriculum plays a pivotal role in nurturing active, healthy, and educated individuals.
1. Active Individuals: The curriculum introduces students to a variety of physical activities, enabling them to explore their interests and passions. By teaching fundamental movement skills and promoting physical fitness, PE programs empower students with the knowledge and confidence to engage in physical activities outside the classroom. This encourages a lifelong commitment to a healthy and active lifestyle (SHAPE America, 2014).
2. Healthy Individuals: The inclusion of health education empowers students to make informed decisions about their health. They gain insights into the benefits of physical activity, nutritional choices, and the risks associated with unhealthy behaviors. This knowledge equips them to lead healthier lives and make choices that reduce the risk of chronic diseases (CDC, 2020).
3. Educated Individuals: Curriculum design in PE extends beyond physical skills; it fosters cognitive development. Through problem-solving in team sports, critical thinking in strategy development, and decision-making in game situations, students develop essential intellectual skills (NASPE, 2009). They also gain a deeper understanding of how physical activity impacts their overall well-being.
In conclusion, Curriculum design in Physical Education is a meticulous and purposeful process that underpins the development of active, healthy, and educated individuals. A well-structured curriculum defines clear learning objectives, incorporates diverse content and activities, utilizes effective assessment and evaluation methods, embraces inclusivity, and imparts health education. Through these components, PE programs contribute not only to physical fitness but also to cognitive, emotional, and social development. By nurturing a love for physical activity, providing students with the knowledge and skills needed for a healthy lifestyle, and aligning with broader educational objectives, PE curriculum design empowers students to lead balanced, fulfilling lives. It equips them with the tools and mindset necessary to make informed choices about their health and well-being, contributing to their success in various facets of life. As such, curriculum design in PE remains a vital and indispensable aspect of the educational journey.
References:
- (2019). Physical Education Curriculum Analysis Tool. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/pecat/index.htm
- (2020). Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool (HECAT).
- Inclusive Fitness Coalition. (2021). Inclusive Physical Education. https://inclusivefitness.org/
- (2020). The Value of Physical Education for Students.
- (2009). Moving into the Future: National Standards for Physical Education (3rd ed.).
- SHAPE America. (2014). National Standards & Grade-Level Outcomes for K-12 Physical Education. https://www.shapeamerica.org/standards/pe/

Former Student at Rajshahi University