Factors of Student Engagement in E-Learning:
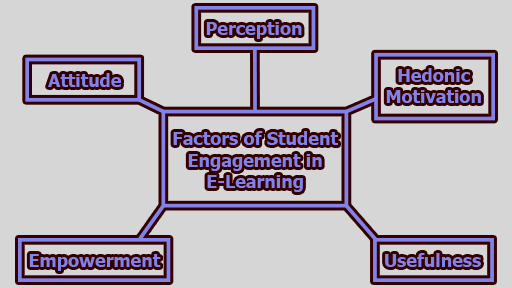
With the advancement of technology and the digital age, e-learning has become an integral part of modern education. The success of online courses depends heavily on student engagement, as active participation is essential for effective learning and academic achievement. Traditional face-to-face learning relies on teachers guiding students, but e-learning shifts the responsibility to learners, making them self-directed, lifelong learners. The engagement of students in the e-learning process is influenced by various factors, which have been extensively researched. This article explores the key factors of student engagement in e-learning, namely Perception, Hedonic Motivation, Usefulness, Empowerment, and Attitude.
1. Perception: Perception is a crucial factor influencing student engagement in e-learning. Students’ perspectives and beliefs about online education can significantly impact their level of involvement in the learning process. Positive perceptions of e-learning can motivate students to actively participate, while negative perceptions may lead to disengagement and reluctance to fully embrace online courses.
One aspect affecting perception is the security and communication systems of virtual classrooms. Incidents such as “Zoom bombing,” where hackers infiltrated online sessions to display inappropriate content, have raised concerns about the safety and privacy of online platforms. To enhance student engagement, developers must prioritize the security and reliability of e-learning tools, thereby addressing students’ fears and promoting a sense of trust and safety.
Furthermore, students’ prior experiences with online education can shape their perceptions. Positive experiences, such as accessing supplemental materials or discovering their learning preferences through e-learning, can foster enthusiasm for online courses. On the other hand, negative experiences, such as poorly designed courses or inadequate teacher-student interaction, can lead to a pessimistic outlook toward e-learning.
Educators and institutions must take into account students’ perceptions and actively address any concerns or challenges they might have about online education. By promoting positive perceptions through well-designed courses, interactive teaching methods, and effective communication strategies, educators can encourage higher levels of student engagement in e-learning.
2. Hedonic Motivation: Hedonic motivation refers to the pleasure and delight students experience while engaging in e-learning. When students find online courses enjoyable and rewarding, they are more likely to stay motivated and committed to their studies. This positive emotional response can significantly impact their level of engagement and academic performance.
To enhance hedonic motivation in e-learning, educators can employ various strategies. Gamification, for instance, involves incorporating game-like elements, such as rewards, challenges, and achievements, into the learning process. By turning learning into a fun and interactive experience, students are more likely to remain engaged and motivated to progress.
Personalization is another important aspect that contributes to hedonic motivation. Tailoring the learning experience to individual student’s interests, preferences, and learning styles can create a sense of ownership and relevance, making the learning journey more enjoyable and rewarding.
Additionally, fostering a sense of community and social interaction within the online learning environment can positively impact hedonic motivation. Collaborative activities, group discussions, and peer feedback can create a supportive and engaging learning community, enhancing students’ motivation and sense of belonging.
3. Usefulness: Perceived usefulness plays a vital role in shaping student engagement in e-learning. When students believe that online courses offer tangible benefits and valuable learning opportunities, they are more likely to actively participate and invest their efforts in the learning process.
E-learning offers several advantages that contribute to its perceived usefulness. One key benefit is the flexibility it provides, allowing students to access course materials and complete assignments at their own pace and convenience. This feature is particularly beneficial for non-traditional students or those with busy schedules.
Moreover, the availability of up-to-date and reliable information in online courses enhances their usefulness. E-learning allows educators to update course content more frequently, ensuring students have access to the latest knowledge and developments in their fields of study.
Furthermore, e-learning’s ability to create global communities and facilitate interactions with peers and experts from diverse backgrounds enhances its perceived usefulness. The opportunity to collaborate and network with individuals worldwide can enrich the learning experience and provide unique perspectives.
To promote perceived usefulness and, consequently, student engagement, educators must emphasize the practical benefits of e-learning and demonstrate how it aligns with students’ academic and professional goals. Clear communication about the advantages of online courses, such as reduced expenses, just-in-time learning, and access to a wide range of resources, can motivate students to actively participate and stay engaged throughout the learning journey.
4. Empowerment: Empowerment in e-learning refers to the extent to which students have control over their own learning experiences. By fostering learner autonomy and interactive learning behaviors, educators can create a more effective and engaging online learning environment.
Giving students greater control over their learning journey can be achieved through various means. For instance, offering a choice in assignments or allowing students to set their own learning goals and pace can empower them to take ownership of their education. Educators can also incorporate self-assessment and reflection opportunities, enabling students to monitor their progress and identify areas for improvement.
Interactive learning behaviors, such as engaging in online discussions, peer-to-peer collaboration, and active participation in virtual classrooms, are integral to empowering students in e-learning. Providing opportunities for teacher-student interaction and constructive feedback can also foster a sense of support and encouragement, promoting learner empowerment.
Additionally, e-learning platforms and tools that offer customization options and adaptive learning features can enhance student empowerment. Adaptive learning technology tailors the learning experience to individual student’s strengths, weaknesses, and learning styles, promoting a more personalized and effective learning journey.
Educators must strive to create a learning environment that encourages and supports student empowerment. By valuing and integrating students’ voices, choices, and perspectives, educators can promote higher levels of engagement and motivation in the e-learning process.
5. Attitude: Attitude encompasses cognitive, affective, and behavioral components that influence student engagement in e-learning. Students’ attitudes toward online education can significantly impact their willingness to participate and invest effort in their studies.
Positive attitudes are conducive to higher levels of engagement and better learning outcomes. Students with positive attitudes are more likely to approach e-learning with enthusiasm, curiosity, and a growth mindset. They are open to exploring new ideas, taking on challenges, and seeking opportunities for personal and academic growth.
On the other hand, negative attitudes can act as barriers to engagement and success in online courses. Students with negative attitudes may feel apprehensive about technology, lack confidence in their abilities, or perceive e-learning as inferior to traditional classroom settings.
To promote positive attitudes toward e-learning, educators can implement the following strategies:
- Provide orientation and training on using online platforms and tools, reducing the fear of technology.
- Offer continuous support and resources to build students’ confidence in their technological skills and ability to succeed in e-learning.
- Design courses that are engaging, interactive, and aligned with students’ interests and learning preferences.
- Foster a positive and inclusive online learning community where students feel valued, supported, and encouraged to share their thoughts and ideas.
- Recognize and celebrate students’ achievements and progress, reinforcing a sense of accomplishment and motivation.
By understanding and addressing students’ attitudes toward e-learning, educators can create a more conducive and supportive learning environment, leading to higher levels of engagement and academic success.
5.1 Behavioral Engagement: Behavioural engagement in e-learning refers to the observable actions and participation of students in online courses. It encompasses the active involvement of students in completing tasks, attending virtual classes, and contributing to discussions and group activities. Behaviourally engaged students demonstrate consistent attendance, timely submission of assignments, and a proactive approach to learning.
One of the key indicators of behavioral engagement is students’ regular attendance and active participation in online sessions. Actively participating in virtual classrooms, engaging in discussions, and asking questions demonstrate a student’s commitment to the learning process. Students who consistently log in to the e-learning platform and complete assignments on time exhibit a higher level of behavioral engagement.
Moreover, students’ willingness to collaborate and work with their peers on group projects or virtual team activities reflects their behavioral engagement. Participating in collaborative activities helps students develop essential teamwork and communication skills while fostering a sense of belonging to a learning community.
To enhance behavioral engagement in e-learning, educators can implement several strategies:
- Clear Communication: Providing clear instructions and expectations about course activities, deadlines, and assessments can help students stay on track and actively participate.
- Active Learning Activities: Incorporating interactive learning activities, such as quizzes, discussions, and simulations, can encourage students to engage with the course content actively.
- Prompt Feedback: Providing timely and constructive feedback on assignments and assessments can motivate students to continue actively participating and improving their performance.
- Encouraging Collaboration: Designing group projects and collaborative tasks can promote teamwork and encourage students to engage actively with their peers.
5.2 Cognitive Engagement: Cognitive engagement in e-learning relates to students’ mental involvement and investment in the learning process. It refers to the degree to which students actively think, process information, and make connections with the course content. Students who are cognitively engaged demonstrate critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deep understanding of the subject matter.
One of the key indicators of cognitive engagement is students’ active participation in discussions and their ability to ask thoughtful questions. Engaged students demonstrate a genuine interest in the course material, seeking to expand their understanding and connect new information with existing knowledge.
Furthermore, students who actively seek out additional resources, conduct research, and explore related topics beyond the course requirements demonstrate cognitive engagement. Such self-directed learning behaviors indicate a higher level of curiosity and motivation to deepen their knowledge.
To enhance cognitive engagement in e-learning, educators can implement several strategies:
- Thought-Provoking Content: Designing course materials that challenge students’ thinking and encourage critical analysis can stimulate cognitive engagement.
- Encourage Reflection: Incorporating reflective activities or journaling prompts can help students process the information and make meaningful connections to their own experiences.
- Support Metacognition: Promoting metacognitive skills, such as goal-setting, planning, and self-assessment, can empower students to take ownership of their learning process.
- Offer Choice and Autonomy: Allowing students to choose topics for research projects or providing options for assignments can foster a sense of autonomy and increase cognitive engagement.
5.3 Emotional Engagement: Emotional engagement in e-learning refers to the affective aspect of students’ involvement in online courses. It involves the feelings, attitudes, and motivation students experience while participating in the learning process. Emotionally engaged students feel positive about their learning experience, exhibit a sense of enjoyment, and develop a connection with the course material and the learning community.
One of the key indicators of emotional engagement is students’ enthusiasm and interest in the course content. When students find the material personally meaningful, relevant, and applicable to their lives, they are more likely to develop a positive emotional connection with the learning experience.
Moreover, the presence of a supportive and inclusive online learning community can significantly impact emotional engagement. Students who feel valued, respected, and connected to their peers and instructors are more likely to be emotionally engaged in e-learning.
To enhance emotional engagement in e-learning, educators can implement several strategies:
- Establish a Positive Learning Environment: Fostering a welcoming and positive online learning environment can create a sense of belonging and emotional connection for students.
- Share Real-World Examples: Relating course concepts to real-life scenarios can help students see the practical applications of the material and foster emotional engagement.
- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledging and celebrating students’ achievements and milestones can reinforce a sense of accomplishment and motivation.
- Provide Supportive Feedback: Offering constructive and encouraging feedback can boost students’ confidence and emotional investment in their learning journey.
In conclusion, Student engagement is a critical factor in the success of e-learning endeavors. Recognizing and understanding the factors that influence student engagement can help educators and course developers create more effective online learning experiences. By addressing students’ perceptions, enhancing their hedonic motivation, emphasizing the usefulness of e-learning, empowering them to take control of their learning, and promoting positive attitudes, we can foster higher levels of engagement and academic accomplishment in online courses. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, prioritizing student engagement remains paramount to the advancement of e-learning and the overall improvement of educational outcomes in the digital era.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQs]:
What is e-learning?
E-learning, short for electronic learning, refers to the process of acquiring knowledge and skills through digital technologies, primarily delivered over the Internet. It involves online courses, virtual classrooms, interactive learning modules, and digital resources that enable learners to access educational content remotely.
How does e-learning work?
E-learning platforms typically host educational content, including lectures, videos, quizzes, and assignments, accessible to students through internet-connected devices such as computers, tablets, or smartphones. Students can engage with the material at their own pace and interact with instructors and peers through discussion forums, video conferencing, and other collaborative tools.
What are the benefits of e-learning?
E-learning offers several advantages, including flexibility in scheduling and location, allowing students to learn at their own convenience. It provides access to a wide range of educational resources and experts worldwide, promoting global collaboration. E-learning is cost-effective as it eliminates the need for physical classrooms and reduces travel expenses.
Is e-learning as effective as traditional classroom learning?
Numerous studies suggest that e-learning can be just as effective as traditional classroom learning when designed and facilitated correctly. The effectiveness of e-learning depends on factors such as course design, instructor engagement, student motivation, and the use of interactive and collaborative learning strategies.
What technology is required for e-learning?
To engage in e-learning, students need a computer, tablet, or smartphone with internet connectivity. Additionally, specific software or learning management systems (LMS) may be required to access course materials, submit assignments, and participate in online discussions.
Can e-learning be personalized to individual learners?
Yes, e-learning can be personalized to individual learners through adaptive learning technologies. These technologies use data and analytics to tailor the learning experience based on student’s strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences, providing customized content and learning pathways.
How can educators promote student engagement in e-learning?
Educators can promote student engagement in e-learning by creating interactive and engaging course materials, incorporating multimedia elements, providing prompt feedback, encouraging peer collaboration, and fostering a supportive online learning community. Additionally, offering choices in assignments and topics can empower students and enhance their motivation to learn.
Is e-learning suitable for all types of courses and subjects?
E-learning can be adapted to a wide range of courses and subjects, but its suitability may vary depending on the content and learning objectives. While certain subjects may require hands-on practical components, many theoretical and knowledge-based courses can be effectively delivered through e-learning platforms.
Are there any challenges associated with e-learning?
Despite its benefits, e-learning also comes with challenges. Some common challenges include technological issues, such as internet connectivity problems or technical glitches, the need for self-discipline and time management skills on the part of learners, and the potential for feelings of isolation due to a lack of face-to-face interactions.
Can e-learning replace traditional classroom learning entirely?
While e-learning has gained significant popularity and acceptance, it is unlikely to completely replace traditional classroom learning. Both approaches have their unique advantages, and a blended learning approach that combines elements of both e-learning and traditional methods often provides the most comprehensive and effective educational experience.
Reference:
Dubey, P., Pradhan, R.L. and Sahu, K.K. (2023), Underlying factors of student engagement to E-learning. Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning, Vol. 16 No. 1, pp. 17-36. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIT-09-2022-0058

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College