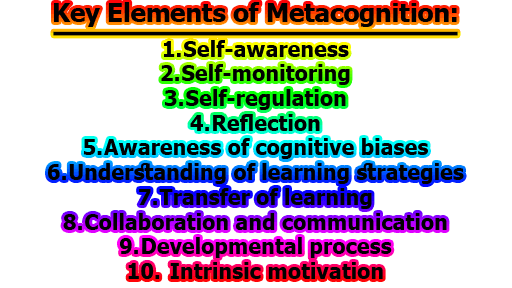
Key Elements of Metacognition:
Metacognition refers to the ability to reflect on one’s own cognitive processes and to monitor and regulate one’s own learning. It involves being aware of one’s own thoughts, knowledge, and understanding, and using that awareness to guide and improve learning and problem-solving. Here are some key elements of metacognition:
1. Self-awareness: Metacognition involves being aware of one’s own thought processes, including strengths and weaknesses, and recognizing when one is not understanding something.
2. Self-monitoring: Metacognition involves monitoring one’s own learning and problem-solving processes, including identifying and correcting errors and adjusting strategies as needed.
3. Self-regulation: Metacognition involves regulating one’s own learning, including setting goals, planning, and managing one’s time effectively.
4. Reflection: Metacognition involves reflecting on one’s own learning experiences and using that reflection to inform future learning and problem-solving.
5. Awareness of cognitive biases: Metacognition involves being aware of one’s own cognitive biases, such as confirmation bias or the sunk cost fallacy, and taking steps to mitigate their effects.
6. Understanding of learning strategies: Metacognition involves understanding and utilizing effective learning strategies, such as elaboration or retrieval practice, to enhance learning and memory.
7. Transfer of learning: Metacognition involves being able to apply knowledge and skills learned in one context to new and unfamiliar situations, a process known as transfer of learning.
8. Collaboration and communication: Metacognition can also involve collaboration and communication with others, such as discussing ideas and problem-solving strategies, and giving and receiving feedback.
9. Developmental process: Metacognition is a developmental process that can be cultivated and improved over time with practice and guidance.
10. Intrinsic motivation: Metacognition can promote intrinsic motivation, as individuals who are more self-aware and reflective may be more likely to pursue activities and goals that align with their interests and values.
Overall, metacognition is a valuable skill that can benefit individuals in a range of contexts, from academic settings to professional and personal life. By becoming more self-aware and reflective learners, individuals can improve their ability to learn, problem-solve, and adapt to new challenges.

Library Lecturer at Nurul Amin Degree College