Trends in Library Automation and Digitalization:
Library automation and digitalization are two of the most important trends that have been transforming the way libraries operate today. With the increasing use of technology in every sphere of our lives, libraries have also been adopting various technologies to make their services more accessible, efficient, and effective. In this article, we will discuss the trends in library automation and digitalization, its impact on libraries and their users, and the challenges that libraries face in implementing these technologies.
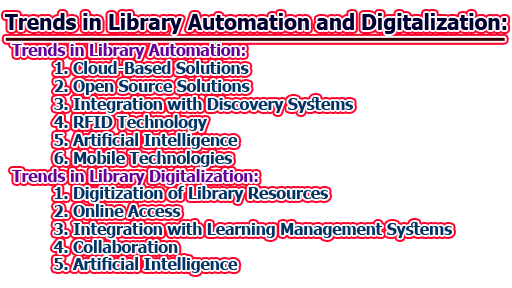
Trends in Library Automation:
The world of libraries has been transformed by the rise of automation technologies. Automation in libraries refers to the use of technology to perform tasks that were previously done manually. This includes tasks such as cataloging, circulation, and inventory management. Library automation has become an essential tool for librarians, enabling them to provide better services to their users. Some of the trends in library automation are given below with a brief description.
1. Cloud-Based Solutions: One of the most significant trends in library automation is the move towards cloud-based solutions. Cloud-based solutions offer several benefits over traditional on-premise solutions. They are more flexible, more scalable, and require fewer resources to maintain. They also offer libraries greater data security and disaster recovery capabilities. Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly popular in libraries of all sizes, as they offer an affordable way to implement automation technologies.
2. Open Source Solutions: Another trend in library automation is the use of open-source solutions. Open-source solutions are software programs that are free to use and can be modified by anyone. They offer libraries several advantages over proprietary software solutions, including greater flexibility and customization capabilities. Open-source solutions are also typically more affordable than proprietary solutions, making them an attractive option for libraries with limited budgets. Many libraries are now using open-source solutions for tasks such as cataloging, circulation, and digital asset management.
3. Integration with Discovery Systems: Library automation systems are increasingly being integrated with discovery systems. Discovery systems are tools that allow users to search for library resources, such as books, journals, and databases, through a single interface. By integrating automation systems with discovery systems, libraries can provide users with a more seamless experience. Users can search for resources, check them out, and access them without leaving the discovery system. This integration also allows libraries to collect more data about user behavior, which can be used to improve services and collections.
4. RFID Technology: Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is another trend in library automation. RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit information between an RFID tag attached to an item and an RFID reader. This technology is increasingly being used in libraries to automate tasks such as check-in, checkout, and inventory management. RFID technology offers several benefits over traditional barcode systems, including faster processing times and the ability to read multiple items simultaneously. It also enables libraries to collect more data about user behavior, which can be used to improve services and collections.
5. Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is another trend in library automation. AI technologies, such as natural language processing and machine learning, can be used to automate tasks such as cataloging and data analysis. They can also be used to improve the user experience by providing personalized recommendations and search results. AI technologies are becoming increasingly popular in libraries, as they offer a way to improve efficiency and provide better services to users.
6. Mobile Technologies: Mobile technologies, such as smartphones and tablets, are also being used to automate library tasks. Mobile technologies can be used to scan barcodes or RFID tags, allowing librarians to perform tasks such as check-in and checkout without being tied to a desk. They can also be used to provide users with access to library resources, such as e-books and databases, from anywhere. Mobile technologies offer libraries greater flexibility and convenience, allowing them to provide better services to users.
Impact of Library Automation:
The impact of library automation has been significant, both for libraries and users. The following are some of the ways in which library automation has affected libraries and users:
- Greater Efficiency: Library automation has greatly increased the efficiency of library operations. Tasks that were once done manually, such as cataloging and circulation, can now be done much more quickly and accurately with automation technologies. This has allowed libraries to provide better services to users, as librarians can focus on more complex tasks, such as collection development and user engagement.
- Improved Access: Library automation has also improved access to library resources for users. With the integration of automation systems with discovery systems and mobile technologies, users can now search for and access library resources from anywhere, at any time. This has made it easier for users to find the resources they need, regardless of their location.
- Better User Experience: The integration of automation technologies with discovery systems and AI technologies has also improved the user experience. Users can now search for resources more easily and receive personalized recommendations and search results. They can also access resources from anywhere, on any device. This has made it easier for users to engage with library resources and has improved overall user satisfaction.
- Increased Data Collection: Library automation has also increased the amount of data that libraries can collect about user behavior. RFID technology and mobile technologies, in particular, allow libraries to collect data about how resources are being used and how users are interacting with library services. This data can be used to improve services and collections and to make data-driven decisions about resource allocation.
- Cost Savings: Library automation can also lead to cost savings for libraries. Cloud-based solutions and open-source software are often more affordable than traditional proprietary solutions. Automation technologies can also reduce the amount of staff time required for tasks such as cataloging and circulation, freeing up staff to focus on other tasks. This can lead to cost savings for libraries, allowing them to invest in other areas, such as collection development.
Challenges and Considerations:
While library automation offers many benefits, there are also challenges and considerations that libraries must take into account when implementing automation technologies. These include the following:
- Data Security: Libraries must ensure that they are protecting user data and maintaining data security when implementing automation technologies. Cloud-based solutions can offer greater security than on-premise solutions, but libraries must still ensure that they are following best practices for data security.
- Staff Training: Implementing automation technologies can require staff training to ensure that staff are comfortable with new systems and processes. Libraries must invest in staff training to ensure that staff are able to use automation technologies effectively.
- Budget: While automation technologies can lead to cost savings in the long run, there may be upfront costs associated with implementing new systems. Libraries must carefully consider their budget when implementing automation technologies and ensure that they are investing in technologies that will provide the greatest benefit to their users.
- Accessibility: Libraries must ensure that automation technologies are accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities. This may require the use of assistive technologies or the development of customized interfaces for users with different needs.
Trends in Library Digitalization:
Library digitalization is the process of converting physical library resources into digital formats and making them available to users through online platforms. With the increasing popularity of digital resources and the growth of online communities, library digitalization has become an important trend in the library world. Some of the trends in library digitalization are given below with a brief explanation.
1. Digitization of Library Resources: The digitization of library resources has been an important trend in library digitalization. Libraries are now digitizing their collections, making them available to users online. Digitization not only increases the accessibility of library resources but also preserves them for future generations. Digitized resources can be easily stored, searched, and accessed from anywhere at any time. This has led to a greater demand for digitization services in libraries.
2. Online Access: With the growth of online communities, libraries are increasingly providing online access to their collections. Online access provides users with the convenience of accessing library resources from anywhere at any time. Online access also allows libraries to reach a wider audience, including those who may not be able to visit physical library locations. This has led to the growth of online library communities and increased engagement with library resources.
3. Integration with Learning Management Systems: Library digitalization has also led to the integration of library resources with learning management systems. This integration provides students with easy access to library resources from within their learning management system. This has led to increased use of library resources and improved student outcomes.
4. Collaboration: Library digitalization has also led to increased collaboration between libraries. Libraries are now able to share resources and collaborate on digitization projects. This has led to a more comprehensive collection of resources and has increased the availability of resources to users.
5. Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) is also becoming an important trend in library digitalization. Libraries are using AI to automate processes such as cataloging and indexing. AI is also being used to improve the searchability of library resources and to provide personalized recommendations to users. This has led to improved user experience and increased engagement with library resources.
Impact of Library Digitalization:
- Increased Accessibility: Library digitalization has increased the accessibility of library resources. Users can now access library resources from anywhere at any time. This has made it easier for users to find the resources they need, regardless of their location. Online access has also made it easier for users with disabilities to access library resources.
- Improved User Experience: Library digitalization has improved the user experience. Digitized resources can be easily searched and accessed online. Online access provides users with the convenience of accessing library resources from anywhere at any time. Integration with learning management systems and the use of AI technologies have also improved the user experience.
- Preservation of Library Resources: Library digitalization has also led to the preservation of library resources. Digitized resources can be easily stored and preserved for future generations. This has led to the preservation of rare and fragile materials that may have been lost over time.
- Increased Collaboration: Library digitalization has increased collaboration between libraries. Libraries are now able to share resources and collaborate on digitization projects. This has led to a more comprehensive collection of resources and has increased the availability of resources to users.
- Cost Savings: Library digitalization can also lead to cost savings for libraries. Online access and digitization can reduce the amount of physical space required for storage and can reduce the need for staff to physically manage resources. This can lead to cost savings for libraries, allowing them to invest in other areas, such as collection development.
Challenges and Considerations:
While library digitalization offers many benefits, there are also challenges and considerations that libraries must take into account when implementing digitalization projects. These include the following:
- Copyright: Libraries must ensure that they have the necessary permissions to digitize and provide online access to copyrighted materials. This can be a complex process and can require negotiations with copyright holders.
- Preservation: While digitization can preserve materials, it is important to ensure that the digital copies are of high quality and that they are stored in a way that ensures their long-term preservation.
- Digital Divide: Library digitalization can exacerbate the digital divide, as users who do not have access to the internet or digital devices may be unable to access digitized library resources.
- Staffing and Training: Library digitalization projects require specialized skills and training. Libraries must ensure that they have the necessary staff and resources to successfully implement digitalization projects.
It is apparent that library automation and digitalization are two important trends that are transforming the library landscape. These technologies provide libraries with greater efficiency, increased accessibility, and improved user experiences. However, implementing these technologies can also present challenges, particularly for libraries operating on limited budgets or in areas with inadequate infrastructure. Addressing these challenges will be key to ensuring that all users can benefit from the many advantages of library automation and digitalization.
References:
- Hardesty, L. (2019). The Future of Libraries: Library Automation. Computers in Libraries, 39(9), 19-22.
- Rehman, S., Kazi, M. A., & Kiyani, M. N. (2020). Impact of Automation on Library Services: A Review. Library Philosophy and Practice, 2020(1), 1-13.
- Rishab, G., & Kumar, M. (2019). Library Automation: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 28(8), 354-360.
- Salahuddin, A., & Afzal, S. (2019). Library Automation and its Benefits in Libraries. International Journal of Library Science and Research, 9(1), 37-43.
- Sathe, T. V., & Jadhav, V. P. (2020). Library Automation: A Review of Recent Trends and Developments. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science, 11(3), 158-166.
- Hirtle, P. B. (2018). Copyright and digitization. College & Research Libraries News, 79(4), 194-197.
- Knuth, R., & VandeCreek, D. (2017). Preservation planning for digitization projects: A white paper. Journal of Library Metadata, 17(1-2), 83-93.
- Liu, X., Chen, Q., & Chen, Y. (2019). A study on the digital divide in China and its implications for library services. Library Hi Tech, 37(3), 448-462.
- Rupp-Serrano, K., & Lange, R. (2019). The staffing and training needs of digitization projects in academic libraries. Journal of Library Administration, 59(7), 753-769.
- Thompson, K. M. (2018). The impact of digitization on academic library collections: A review of the literature. College & Research Libraries, 79(5), 619-637.

Former Student at Rajshahi University