Marketing research is the systemic process of collecting, recording, analyzing the information relevant to finding a solution to a problem in the field of marketing. The goal of marketing research is to provide the facts and direction that managers need to make their more important marketing decisions. In the rest of the article, we are going to present you types of marketing research
“Marketing research is the function which links the consumers, customers, and publics to the market through information – information used to identify and define marketing opportunities and problems, generate, refine, and evaluate marketing actions, monitoring marketing performance, and improve understanding of marketing as a process.” (American Marketing Association)
Marketing research is the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data, and findings relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the organization.
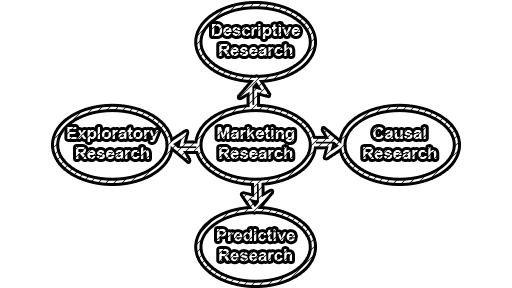
Types of Marketing Research:
There are different types of marketing research classified on the research objective for which study is to be carried out and sources of data used to gather the information. The widely used classification of marketing research and are identified as:
i. Exploratory Market Research: The researcher uses exploratory research when he/she has very little information about the research problem and needs to gain insights about it before finding the solution. It requires the researcher to clear his/her concept, gain insights, formulate problems, eliminating impractical ideas, and formulate a hypothesis to check the relevancy of the research design. This can be done by using the organization, conducting observational studies, consulting experts, and processing feedback from the marketplace and surveys.
ii. Descriptive Market Research: Descriptive research is concerned with testing the hypothesis to find out the accurate answers to the research problem, such as;
- Who are the prospective buyers of the product?
- How the products are consumed?
- What fraction of the population uses the product?
- What is the demand forecast?
- Who are the potential competitors?
The objective of the descriptive market research is to measure the frequency with which things occur and the extent to which the variables under study are correlated.
iii. Causal Market Research: The casual market research is conducted to establish the cause-and-effect relationship between the variables, such as if the packaging of the product is changed then what will be its effect on the product durability? Thus, this research is carried out to explain the facts that’s why a certain change in one variable is observed due to the change in the order.
iv. Predictive Market Research: As the name suggests, predictive research is conducted to forecast or predict certain market variables for which the research is designed. Such as predicting the future, sales, projection of growth, test market to predict the success of a new product, defining of firm’s product line, etc.
Need purposes of Marketing Research:
Some need purposes of marketing research are as follows:
- To help firms make marketing decisions.
- It helps to reduce risk.
- It helps to take decisions in a convenient way.
- To improve the quality of decision-making.
- Information can be collected through marketing research.
The Value of Information in Marketing Research:
Information can be useful, but what determines its real value to the organization? In general, the value of information is determined by:
- The ability and willingness to act on the information.
- The accuracy of the information.
- The level of indecisiveness that would exist without the information.
- The amount of variation in the possible results.
- The level of risk aversion.
- The reaction of competitors to any decision is improved by the information.
- The cost of the information in terms of time and money.
The information helps in Marketing Research:
Some key fact’s information to help in marketing research are given below:
- Identify potential new customers.
- Understand your existing customers by market research.
- Set realistic targets for your business.
- Develop new effective strategies by understanding your market.
- Solve your main business challenges.
- Prepare for possible business expansion by getting the right data.
- Identify new business opportunities by identifying gaps in their offer.
Process of Marketing Research:
Some of the major steps involved in the marketing research process are as follows:
a) Identification and Defining the Problem: Clear definition of the problem helps the researcher in all subsequent research efforts including setting proper research objectives, the determination of the techniques to be used, and the extent of information to be collected. Survey of secondary date, experience survey, or pilot studies, i.e. studies of a small initial sample. All this is also known as ‘Preliminary investigation’.
b) Statement of Research Objectives: A hypothesis is a statement that can be refuted or supported by empirical findings. The same research objective could be stated as, “to test the proposition that sales are positively affected by the sales promotion schemes undertaken this winter.” An example of another hypothesis may be, “the new packaging pattern has resulted in an increase in sales and profits.” Once the objectives or the hypotheses are developed the researcher is ready to choose the researcher design.
c) Designing the Research Study: The objectives of the study are included in the research design to ensure that the data collected are relevant to the objectives. At this stage, the researcher should also determine the type of sources of information needed, the data collection method, the sampling, methodology, and the timing and possible costs of research.
d) Planning the sample: Sampling involves procedures that use a small number of items or parts of the ‘population’ to make a conclusion regarding the ‘population’. Important questions in this regard are – Who is to be sampled as a rightly representative lot? Which is the target ‘population’? What should be the sample size – how large or how small? How to select the various units to make up the sample?
e) Data Collection: The collection of data relates to the gathering of facts to be used in solving the problem. Hence, methods of market research are essentially methods of data collection. Data can be secondary, i.e. collected from concerned reports, magazines, and other periodicals, especially written articles, government publications, company publications, books, etc. There can be broadly two types of sources.
- Internal sources: existing within the firm itself, such as accounting data, salesmen’s reports, etc.
- External sources: outside the firm.
f) Data Processing and Analysis: Once data have been collected, these have to be converted into a format that will suggest answers to the initially identified and defined problem. Data processing begins with the editing of data and its coding. Analysis of data represents the application of logic to the understanding of data collected about the subject. In its simplest form analysis may involve the determination of consistent patterns and summarize of appropriate details.
g) Prepare the Research Report: The final stage in the marketing research is that of interpreting the information and drawing conclusions for use in managerial decisions. The research report should clearly and effectively communicate the research findings and need not include complicated statements about the technical aspect of the study and research methods. Researchers must make the presentation technically accurate, understandable, and useful.
Objectives of Marketing Research:
Some of the necessary objectives of marketing research are as follows;
- Identify the consumer response to the company’s product.
- Know the consumer’s needs and expectations.
- Seek maximum information about the customer.
- Check the reaction of the dealer to the company policies.
- Evaluate the reputation of the company in the market.
- Search for new marketing opportunities.
- Find out alternative uses of the existing products.
- Estimate the cost of marketing goods and services.
- Supply up-to-date information about market trends, demands and supply position, etc.
- Forecast the future sales and business conditions.
Advantages of Marketing Research:
- Helps focus attention on objectives.
- Aids forecasting, planning, and strategic development.
- May help to reduce the risk of new product development.
- Communicates image, vision, etc.
- Globalization makes market information valuable.
Disadvantages of Marketing Research:
- Information is only as good as the methodology used.
- Can be inaccurate or unreliable.
- Results may not be what the business wants to bear.
- May stifle initiative and ‘gut feeling’.
- Always a problem that we may never know enough to be sure of.
Marketing research by itself does not arrive at marketing decisions, nor does it guarantee the organization will be successful in marketing its products. However, when conducted in a systematic analytical, and objective manner, marketing research can reduce the uncertainty in the decision-making process and increase the probability and magnitude of success.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College