In an academic context, an assignment is a task or project given to students by their teachers or professors. Academic assignments can take many different forms, such as essays, research papers, lab reports, case studies, presentations, and more. The purpose of academic assignments is to help students develop their critical thinking, research, writing, and communication skills. These assignments are usually graded, and the results can contribute to a student’s overall academic performance. Academic assignments can be designed to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or subject, to encourage students to explore a topic in-depth or to develop a specific skill or set of skills. The requirements and guidelines for academic assignments can vary depending on the institution, department, and course. It is important for students to carefully read and follow the instructions provided by their instructors, and to seek clarification if needed.
Definitions of Academic Assignment:
Here are some definitions of academic assignments from different writers:
According to The Writing Center at UNC-Chapel Hill, an academic assignment is “a specific task or written piece of work that students complete during their studies, such as an essay, research paper, case study, or lab report.”
The University of Reading describes an academic assignment as “a piece of work that is usually written, although there are also oral assignments, such as presentations or group projects. Assignments can be formative (for learning) or summative (for assessment).”
In their book “The Study Skills Handbook,” Stella Cottrell and Kate Williams define academic assignments as “tasks set by tutors or lecturers as part of a course of study. They are intended to help you learn and develop your understanding, knowledge, and skills.”
The University of Melbourne’s Academic Skills website defines academic assignments as “tasks that students are expected to complete during their studies, usually involving the creation of a written piece of work, but sometimes including oral presentations or group projects. Assignments can be used to assess a student’s understanding and mastery of a particular topic, as well as their critical thinking and analytical skills.”
The Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) defines academic assignments as “tasks that students complete as part of their coursework, which can include essays, research papers, case studies, and other types of written work. These assignments are designed to help students develop their research, writing, and critical thinking skills.”
From the above definitions, we can say that an academic assignment is a learning activity designed to test a student’s knowledge, understanding, and skills in a particular subject or topic. These assignments can take many forms, such as essays, case studies, group projects, and research papers. The purpose of academic assignments is to help students develop their critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
Types of Academic Assignment:
Academic assignments can take many forms, depending on the level of education and the specific course or program of study. Here are the types of academic assignments commonly assigned at different levels of education:
- School assignments: These are academic tasks given to students in primary or secondary school. School assignments may include reading comprehension exercises, math problems, writing assignments, research projects, and group presentations. These assignments are usually designed to reinforce the concepts and skills taught in class and to help students develop their critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- College assignments: College assignments are given to students in post-secondary institutions, such as community colleges and vocational schools. These assignments may include essays, research papers, case studies, lab reports, and group projects. College assignments are designed to challenge students to think critically, analyze information, and apply their knowledge and skills to real-world problems.
- University assignments: University assignments are given to students in undergraduate or graduate programs at universities. These assignments may include essays, research papers, literature reviews, case studies, dissertations, and group projects. University assignments are designed to help students develop their research and writing skills, as well as their ability to analyze complex information and synthesize ideas.
Some common features of academic assignments at all levels include clear instructions, deadlines, and specific requirements for formatting, citation, and referencing. Additionally, assignments may be designed to assess a student’s knowledge and understanding of a particular subject or topic, to encourage students to explore a topic in-depth or to develop a specific skill or set of skills. It is important for students to carefully read and follow the instructions provided by their instructors, and to seek clarification if needed.
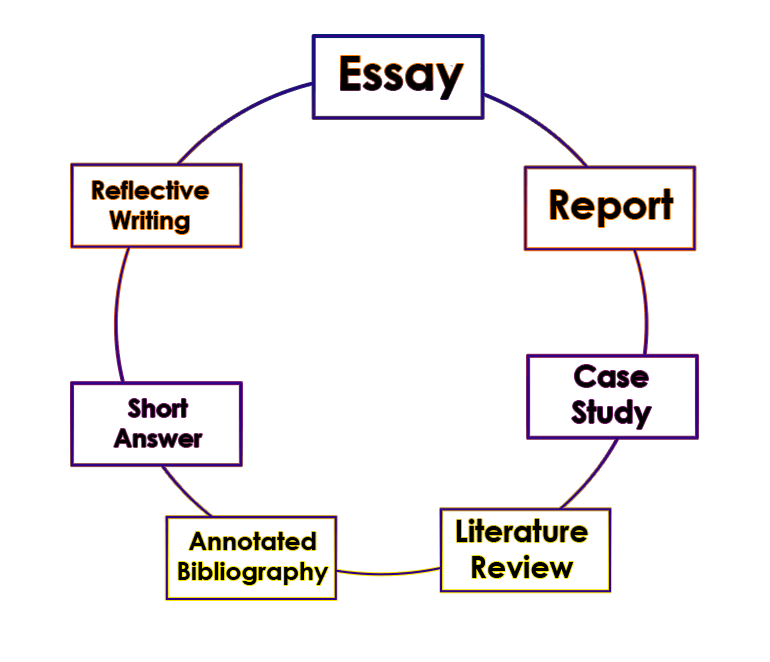
Types of University Assignment:
University assignments come in a variety of formats and types, depending on the course and program of study. Here are some of the most common types of university assignments:
a. Essay: An essay is a type of academic assignment in which the student is asked to present an argument or discuss a topic in a structured format. Essays typically have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, and require the use of evidence and research to support the argument.
b. Report: A report is a type of academic assignment that involves presenting information on a specific topic or issue. Reports may include sections such as an introduction, background, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
c. Case study: A case study is a type of academic assignment that involves analyzing a specific case or situation in depth. Case studies may require the student to identify key issues, analyze data, and propose solutions or recommendations.
d. Literature review: A literature review is a type of academic assignment in which the student is asked to review and analyze existing research on a particular topic or issue. Literature reviews require the use of academic sources and the synthesis of information from multiple sources.
e. Annotated bibliography: An annotated bibliography is a type of academic assignment that involves compiling a list of sources on a particular topic, along with a brief summary and evaluation of each source.
f. Short answer: A short answer assignment typically involves answering a series of questions in a brief, concise format. Short answer assignments may test the student’s knowledge of a particular topic or concept.
g. Reflective writing: Reflective writing is a type of academic assignment in which the student is asked to reflect on their own learning or experiences. Reflective writing may involve analyzing personal experiences, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and developing strategies for future learning.
Each type of university assignment requires different skills and approaches, and may have specific requirements for formatting, citation, and referencing. It is important for students to carefully read and follow the instructions provided by their instructors, and to seek clarification if needed.
Purposes of Academic Assignment:
Academic assignments serve several important purposes for students, instructors, and the educational system as a whole. Here are some of the main purposes of academic assignments:
- Assessing student learning: Academic assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding and mastery of a particular topic or concept. Assignments can help instructors identify areas where students may need additional support or clarification, and can provide a basis for assigning grades and determining academic progress.
- Developing critical thinking skills: Academic assignments often require students to analyze information, evaluate evidence, and make reasoned arguments. These skills are essential for success in many academic disciplines, as well as in the workplace and in everyday life.
- Encouraging creativity and originality: Many academic assignments allow students to express their own ideas and perspectives, and to develop creative solutions to complex problems. Assignments that require research and independent thinking can help students develop their own voice and style, and can foster a sense of intellectual curiosity and engagement.
- Developing research and writing skills: Academic assignments often require students to conduct research, analyze data, and present their findings in a clear and organized manner. These skills are essential for success in many academic and professional fields and can help students develop confidence and competence in writing and research.
- Providing opportunities for feedback and revision: Academic assignments often involve a process of feedback and revision, in which students receive feedback from their instructors and peers, and have the opportunity to revise and improve their work. This process can help students develop a growth mindset and a sense of continuous improvement, and can lead to deeper understanding and better academic performance.
Characteristics of Academic Assignment:
Academic assignments have several distinctive characteristics that set them apart from other types of writing or tasks. Here are some of the key characteristics of academic assignments:
- Purpose: Academic assignments are typically designed to serve a specific purpose, such as assessing student learning, developing critical thinking skills, or promoting creativity and originality. This purpose is often communicated clearly to students through assignment instructions or course materials.
- Structure: Academic assignments often have a clear and structured format, with specific requirements for length, formatting, citation, and referencing. These requirements may vary depending on the type of assignment, the course, or the instructor, but they generally provide a framework for students to follow.
- Audience: Academic assignments are usually written for a specific audience, such as the instructor or the broader academic community. Students are expected to demonstrate an awareness of their audience and to use appropriate language and tone in their writing.
- Research: Many academic assignments require students to conduct research, analyze data, or draw on existing academic literature. This research is typically conducted using reliable and credible sources, and is integrated into the assignment in a clear and meaningful way.
- Evidence: Academic assignments typically require the use of evidence to support arguments or claims. This evidence may come from academic sources, personal experiences, or other types of research, and must be integrated into the assignment in a logical and coherent manner.
- Critical thinking: Academic assignments often require students to engage in critical thinking, such as analyzing information, evaluating evidence, and making reasoned arguments. This critical thinking is often one of the key learning outcomes of the assignment.
- Revision: Academic assignments often involve a process of feedback and revision, in which students receive feedback on their work and have the opportunity to revise and improve it. This process of revision is designed to help students develop their writing and critical thinking skills, and to promote continuous improvement.
Rules of Writing an Academic Assignment:
Writing an academic assignment requires adherence to certain rules and guidelines to ensure that it meets the expectations of instructors and the academic community. Here are some of the key rules of writing an academic assignment:
i. Understand the assignment: Before starting to write, make sure you fully understand the assignment instructions, including the topic, length, format, and deadline. Clarify any questions or uncertainties with your instructor before beginning.
ii. Use credible sources: Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites to support your arguments and claims. Avoid unreliable sources such as blogs or non-peer-reviewed websites.
iii. Follow citation and referencing guidelines: Properly cite and reference all sources used in the assignment according to the appropriate citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago. This helps to avoid plagiarism and shows your credibility and professionalism.
iv. Organize your writing: Use a clear and logical structure that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Use headings and subheadings to make the organization clear to the reader.
v. Use formal language: Use formal language and avoid contractions, slang, or colloquialisms. This helps to maintain a professional tone and shows your respect for the academic community.
vi. Proofread and revise: Edit your work carefully for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Revise your work to ensure that your arguments are clear, well-supported, and well-organized.
vii. Avoid plagiarism: Make sure that all ideas and information that are not your own are properly cited and referenced. Plagiarism is a serious academic offense and can result in severe consequences.
viii. Follow formatting guidelines: Follow any formatting guidelines provided by your instructor, such as font size, margins, and spacing. This helps to ensure that your work is presented in a professional and consistent manner.
By following these rules, you can ensure that your academic assignment meets the expectations of your instructor and the academic community and demonstrates your knowledge and skills effectively.
Factors to Consider for Academic Assignment:
When working on an academic assignment, there are several factors that you should consider to ensure that you produce high-quality work that meets the expectations of your instructor and the academic community. Here are some of the key factors to consider:
- Assignment instructions: Read the assignment instructions carefully to make sure you understand the requirements, expectations, and guidelines for the assignment.
- Audience: Consider your audience, which may include your instructor and other members of the academic community. Think about their expectations, knowledge level, and areas of interest when crafting your assignment.
- Purpose: Consider the purpose of the assignment, which may be to demonstrate your understanding of a topic, analyze a problem, or argue a point of view. Make sure your work addresses the purpose of the assignment clearly and effectively.
- Topic selection: Choose a topic that is interesting, relevant, and manageable. Make sure your topic is appropriate for the assignment and aligns with the assignment instructions.
- Research: Conduct thorough research using reliable sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites. Make sure to critically evaluate and analyze the sources you use to ensure they are relevant and credible.
- Organization: Organize your assignment effectively, using a clear and logical structure that includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. Use headings and subheadings to make your organization clear to the reader.
- Writing style: Use a formal writing style appropriate for academic writing. Avoid using slang, colloquialisms, or contractions. Use clear, concise language to convey your ideas effectively.
- Citation and referencing: Properly cite and reference all sources used in your assignment according to the appropriate citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago. This helps to avoid plagiarism and shows your credibility and professionalism.
- Editing and proofreading: Edit and proofread your work carefully to ensure that it is free from errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Consider having someone else review your work as well to get a fresh perspective.
By considering these factors, you can produce an academic assignment that is well-researched, well-organized, and effectively communicates your ideas to your intended audience.
Academic Assignment Writing Process:
The academic assignment writing process involves several steps that can help you produce high-quality work that meets the expectations of your instructor and the academic community. Here are some of the key steps involved in the academic assignment writing process:
- Understanding the assignment: Before beginning your assignment, read and understand the assignment instructions carefully. Identify the purpose of the assignment, the audience, the format, the length, and the deadline.
- Topic selection: Choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to you and aligns with the assignment instructions. Conduct preliminary research to determine if there are enough credible sources available to support your argument.
- Research: Conduct thorough research using reliable sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites. Take detailed notes and keep track of your sources.
- Organize your ideas: Organize your ideas and notes into an outline or mind map. Use this to develop a clear and logical structure for your assignment.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment, starting with an introduction that provides background information and a clear thesis statement. Use the outline or mind map to guide your writing and organize your ideas.
- Edit and revise: Edit and revise your draft, checking for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Make sure your ideas are clear, well-supported, and well-organized. Consider having someone else review your work to get a fresh perspective.
- Finalize your assignment: Make final revisions and proofread your work. Ensure that you have properly cited and referenced all sources used in your assignment. Follow any formatting guidelines provided by your instructor.
Remember to give yourself enough time to complete each step of the process to ensure that you produce the best possible work.
Finally, we can say that academic assignment is the process of defining, selecting, designing, collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and using the information for students learning and development. It is important to think about the academic assignment in the context of the selected course. It is ensuring that students have experiences both in and outside their courses that help them achieve the intended learning outcomes. Besides academic assignment improves individual student performance.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College