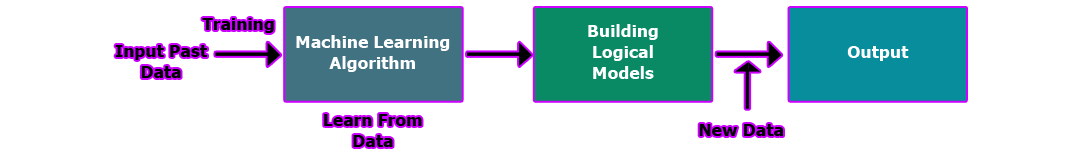
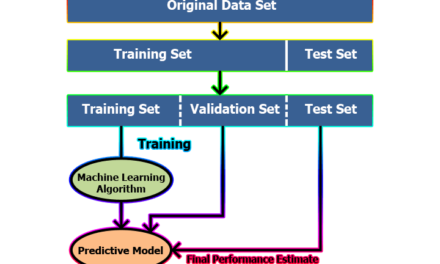
Machine Learning:
Machine Learning is a cutting-edge discipline situated at the confluence of computer science and statistics. It revolutionizes the way computers assimilate and adapt from data, imbuing them with the capability to enhance their performance through iterative learning processes. Rooted in the concept of enabling systems to autonomously refine their understanding, Machine Learning heralds a new era of automation and informed decision-making. By harnessing advanced algorithms and data-driven insights, it empowers computers to transcend conventional programming paradigms, thereby reshaping industries and propelling technological frontiers forward. In the rest of this article, we are going to know about understanding machine learning, how does machine learning work, understanding, features, needs, and types of machine learning.
Understanding Machine Learning:
In the real world, we have people who learn things from their experiences, and we also have machines that do what we tell them to do. But what if machines could learn from their experiences too, just like people do? This is where Machine Learning comes in.
Think of Machine Learning as a special part of computer smarts. It’s like teaching computers to learn on their own from information and stuff that happened before. The term “Machine Learning” was first used by a person named Arthur Samuel in 1959. In simple words, it means making machines smarter by letting them learn from data, getting better with experience, and guessing things without us having to tell them every single detail.
Imagine having a bunch of old information, like a storybook of the past. Machine Learning uses this old information to create a kind of magic math model. This model helps machines make good guesses and choices without someone telling them exactly what to do. It’s like when you know a lot of stories, you become good at guessing what happens next in a new story.
Machine Learning mixes computer science and math tricks to create these smart models. Machines learn from the old stories and use this knowledge to understand new things. And guess what? The more stories we give the machines, the better they become at guessing and understanding things.
Just like when you learn more things, you get smarter, machines also learn more and get better as they see more data. This exciting blend of data and computer magic makes Machine Learning a powerful tool that can change how machines help us in the future.
How Does Machine Learning Work:
Machine Learning is like a smart student that learns from old lessons, figures out patterns, and then makes predictions about new things. Imagine it as a puzzle solver – it looks at lots of pieces of information and uses those pieces to guess what should come next.
Suppose you have a tricky problem to solve, and instead of writing a step-by-step solution, you give the problem and some examples to a special computer program. This program uses its magic to figure out the solution by looking at those examples. It’s like letting the computer learn from the examples instead of telling it exactly what to do.
Think of Machine Learning like this: you have a detective who looks at a lot of clues and then figures out what happened. The more clues they have, the better their answer. Machine Learning is like giving the detective a lot of clues (data), and they use those clues to solve mysteries and make smart guesses. It’s a way of making computers really good at understanding and solving problems without us having to write out all the steps.
Features of Machine Learning:
a. Pattern Detective: Machine Learning is like a detective for patterns. Imagine it looking at a big puzzle made of information and finding hidden shapes or designs in the pieces. It’s really good at spotting interesting things in a bunch of data.
b. Smart Learner: Think of Machine Learning as a smart student. It learns from its mistakes and gets better without anyone teaching it again. Just like you learn from your experiences, it learns from the data it sees.
c. Data Lover: Machine Learning is all about data – it’s like its favorite snack. It uses information to become more knowledgeable and skillful. The more data it has, the smarter it gets.
d. Treasure Hunter: Just like treasure hunters dig through a lot of stuff to find valuable things, Machine Learning deals with lots of data to find the important bits. It’s really good at finding those hidden gems of information.
e. Predictive Magic: Imagine Machine Learning as a magician’s crystal ball. It uses data to understand things so well that it can predict what might happen in the future. It’s like guessing the next plot twist in a story, but with data!
f. Curious Friend: Machine Learning is like that curious friend who always asks a lot of questions. It wants to know everything it can from the data it’s given. The more it knows, the better it can solve problems and give you answers.
g. Problem Solver: Consider Machine Learning as a super problem solver. Instead of telling it exactly what to do, you give it examples and it figures out the solution on its own. It’s like having a helper that can think and learn just like you.
In a nutshell, Machine Learning is like having a smart detective-friend who loves data, learns from it, and uses its knowledge to solve mysteries and predict outcomes.
Needs for Machine Learning:
Machine Learning has become more and more important with each passing day. The reason is simple: it can do tasks that are just too tough for humans to handle all by themselves. Imagine trying to manage a massive pile of information all on your own – it’s like trying to read a thousand books in a day. That’s where Machine Learning steps in to lend a helping hand.
See, humans have their limits. We can’t dig through enormous amounts of data all by hand. But computers can, Machine Learning makes things easier by letting computers handle the heavy lifting. We teach special computer systems by showing them lots of data and letting them explore it. They build smart models and figure out answers automatically. It’s a bit like training a super detective to solve cases.
The more data these computer systems get, the better they become at their jobs. Imagine them as super learners, getting better every time they see new information. And guess what? Machine Learning saves us both time and money. It’s like having a super assistant who’s always ready to help.
Think about this: Machine Learning is behind those cool self-driving cars, catching cyber bad guys, recognizing faces, and suggesting friends on Facebook. Even big companies like Netflix and Amazon use Machine Learning to learn what we like and recommend stuff we might enjoy.
Here are some important points to remember about Machine Learning:
- The more data we have, the more Machine Learning shines.
- It’s like a superhero solving really tough problems.
- It helps make important decisions, even in finance.
- Imagine it as a code breaker – finding secret patterns in data that humans might miss.
Types of Machine Learning:
Machine Learning can be thought of as a toolbox with different methods for computers to learn and improve. Let’s delve into the three main types:
1. Supervised Learning: Guided Learning: Imagine you’re a teacher showing a student examples of different animals and telling them which ones are cats and which are dogs. In supervised learning, we guide the computer by giving it labeled data. This means we provide the computer with input data and the correct output it should predict. The computer learns from this combination and builds a model that can predict the right answers for new, unseen data. Just like a student practices with homework and learns from the teacher’s feedback, the computer becomes better at making predictions over time.
Categories within Supervised Learning:
- Classification: Think of this as sorting things into different groups. Like sorting emails into “important” and “spam.”
- Regression: It’s like predicting numbers on a scale, such as estimating the price of a house based on its features.
2. Unsupervised Learning: Self-Exploration: Now, imagine you’re exploring a new place without a map or guide. Unsupervised learning is similar. Here, the computer isn’t given labeled data. Instead, it explores and tries to find patterns on its own. It groups similar things together and discovers hidden relationships within the data. It’s like discovering that certain people in your class share similar hobbies without anyone telling you. This type of learning is excellent for uncovering insights and structuring data.
Categories within Unsupervised Learning:
- Clustering: The computer groups similar things together, even when we didn’t tell it what the groups should be.
- Association: It finds connections between items, like suggesting products that people often buy together.
3. Reinforcement Learning: Learning from Experience: Imagine you’re training a puppy to do tricks. When it follows a command correctly, you give it a treat. If it makes a mistake, you correct it. Reinforcement learning works similarly. The computer, acting as an agent, interacts with an environment and learns by receiving rewards for correct actions and penalties for wrong ones. Over time, it learns to take actions that maximize rewards and minimize penalties, much like a person learning to play a video game better with practice.
Reinforcement learning is powerful for scenarios where learning from experience is key, such as training self-driving cars to navigate complex roads.
In brief, Machine Learning offers these three methods to teach computers:
- Supervised Learning for guided predictions.
- Unsupervised Learning for finding hidden patterns.
- Reinforcement Learning for learning from rewards and penalties.
Together, these types empower computers to handle a wide range of tasks and become smarter with every interaction.
In conclusion, Machine Learning offers a dynamic set of approaches that empower computers to learn, adapt, and make informed decisions in various scenarios. Just as a student gains knowledge through guided learning, exploration, and experience, computers are equipped with the tools to comprehend complex data, uncover hidden patterns, and optimize actions. Supervised learning acts as a guiding hand, while unsupervised learning allows computers to independently explore data landscapes. Reinforcement learning, akin to a learning process grounded in rewards and penalties, enables computers to navigate real-world environments. Together, these types of Machine Learning form a comprehensive toolkit that reshapes industries, accelerates problem-solving, and fuels the advancement of intelligent systems. With each method playing a unique role, Machine Learning promises an exciting journey into a future where computers not only assist but actively participate in enhancing our understanding and shaping the world around us.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College