Special Features of the DDC Scheme:
The Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC) is a renowned and universal scheme of library classification used worldwide in libraries and information centers. It offers a systematic approach to organizing diverse subjects, accommodating various formats such as books, journals, audiovisual materials, and electronic resources. The DDC employs several distinctive features that make it an efficient and flexible system for users to navigate through vast collections. In this article, we will delve into the special features of the DDC scheme.
1. Universal Scheme: The Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC) is universally recognized as a comprehensive and versatile classification system. Its universal nature allows it to encompass an extensive range of subjects from various domains and cultures. This inclusiveness makes the DDC suitable for libraries and information centers worldwide, accommodating diverse collections that serve the needs of a broad user base.
The DDC covers subjects from traditional academic disciplines like history, literature, and science to more contemporary and specialized areas such as computer science, environmental studies, and social media. Furthermore, it can be used in different types of libraries, including public, academic, school, and special libraries. The ability to accommodate diverse subjects and cater to various library types makes the DDC a widely adopted and adaptable classification system.
2. Relative Location: In the DDC, subjects are arranged based on their relative relationships to one another. When a user searches for a specific topic, they will find related subjects positioned close to the main subject in the classification scheme. For example, if a reader is interested in the history of ancient civilizations (e.g., Egypt), they can easily navigate to related subjects like archaeology, ancient art, or world history.
This feature fosters serendipitous discovery, encouraging users to explore related topics and find materials they might not have thought of initially. It promotes interdisciplinary research and provides a more holistic approach to knowledge discovery within a library’s collection.
3. Decimal Notation: The DDC employs a decimal notation system, representing each subject category with a whole number and further dividing it into specific subdivisions using decimal numbers. This hierarchical system allows for the precise classification of subjects, making it easier for users to find information on specific topics.
For instance, if a library has a book on marine biology, it would be classified under the number 577 in the DDC, where 500 represents natural sciences and mathematics, and 577 denotes the specific field of marine biology. The use of decimal numbers allows for infinite potential subdivisions within each main class, ensuring that materials can be accurately classified based on their subject matter.
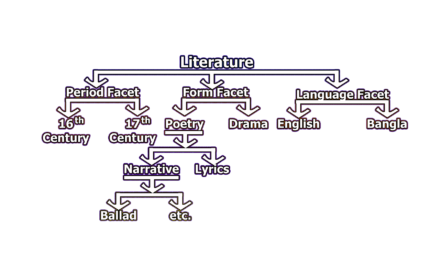
4. Minute Division: The DDC is renowned for its minute division of subjects, enabling precise classification of even highly specialized topics. This feature is particularly advantageous for libraries with extensive and diverse collections.
For example, under the general category of literature (800), one can find divisions for various literary forms, such as drama, poetry, and fiction. Subsequently, under fiction (813), one can find subdivisions for American fiction, English fiction, and so on, creating a highly detailed and organized system.
This minute division ensures that users can quickly locate materials pertaining to their specific research interests, promoting efficiency and accuracy in information retrieval.
5. Mnemonics: The DDC incorporates mnemonics or memory aids to make it easier for users to remember the main classes and their corresponding numbers. These mnemonic devices are especially helpful for library staff, researchers, and students who need to navigate the classification system frequently.
For instance, the number 500 is assigned to natural sciences and mathematics because it starts with the letter “N,” which is the first letter of the word “natural.” Similarly, the number 900 represents history and geography because “history” and “geography” both start with the letter “H.”
These simple and intuitive memory aids simplify the classification process, making it user-friendly and accessible to all.
6. Integrity of Numbers: The DDC ensures the integrity of numbers, which means that each number corresponds to a unique subject. This principle is crucial for avoiding confusion and maintaining consistency within the classification system.
When a new subject emerges, it is carefully analyzed, and if it does not fit existing classifications, a new number is assigned to it. This ensures that materials are accurately placed within the scheme, making it easier for users to locate them based on their topics.
Additionally, the DDC allows for the combination of numbers to represent compound subjects. For example, the number 623.8 represents naval architecture, and the number 623.82 represents shipbuilding. By combining these numbers, the compound subject of naval architecture and shipbuilding is represented by the number 623.82.
7. Auxiliary Tables: In addition to the main classification schedule, the DDC offers auxiliary tables that enhance the classification of specific subject areas. These tables provide additional guidance for classifying materials that might not fit neatly into the primary schedule.
For example, the tables for geographic areas aid in classifying materials related to specific countries or regions. The tables for literary forms and genres help categorize works of fiction, poetry, drama, and more. Similarly, tables for languages assist in classifying materials written in different languages.
The inclusion of these auxiliary tables makes the DDC more adaptable to various types of collections and user needs. Libraries with specialized or multicultural collections can effectively organize their materials using these supplementary tools, ensuring that materials are appropriately classified and accessible to users.
In conclusion, the Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC) stands as a universal and versatile scheme of classification, facilitating the systematic arrangement and retrieval of information in libraries and information centers worldwide. With its distinctive features, such as relative location, decimal notation, mnemonics, and auxiliary tables, the DDC enables users to navigate through a vast array of subjects, discovering related topics, and locating precise information efficiently. Its meticulous design ensures the integrity of numbers and allows for minute division, making it an indispensable tool for organizing knowledge and enhancing the research experience. The DDC continues to serve as an indispensable and enduring system, contributing to the ease of access and dissemination of knowledge across the globe.

Library Lecturer at Nurul Amin Degree College