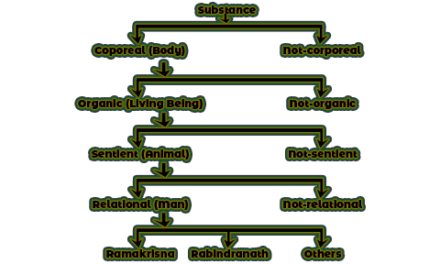
Number Building Process in DDC:
DDC stands for Dewey Decimal Classification, which is a system used for classifying books and other materials in libraries. The DDC system is based on a hierarchical structure, in which subjects are divided into broad categories, and then into increasingly specific subcategories. The number building process in DDC involves creating a unique call number for a specific item, based on its subject content.
Basic Structure of DDC: DDC mainly consists of ten main classes, every main class has ten divisions and every division has ten sections.
The ten main classes of DDC 23rd edition are:
000 – Computer science, information, and general works
100 – Philosophy and psychology
200 – Religion
300 – Social sciences
400 – Language
500 – Natural sciences and mathematics
600 – Technology (Applied sciences)
700 – Arts and recreation
800 – Literature
900 – History and Geography
Each main class is divided into ten divisions: (there are a hundred divisions in DDC)
000 – Computer science, information, and general works
010 – Bibliography
020 – Library and information sciences
030 – Encyclopedias and books of facts
040 – [Unassigned]
050 – Magazines, journals, and serials
060 – Associations, organizations, and museums
070 – News media, journalism, and publishing
080 – Quotations
090 – Manuscripts and rare books
Each division is divided into ten sections: There are a thousand sections in DDC.
800 – Literature
820 – English and Old English literature
821 – English poetry
822 – English drama
823 – English fiction
824 – English essays
825 – English speeches
826 – English letters
827 – English satire and humor
828 – English miscellaneous writings
829 – Old English (Anglo-Saxon) literature
Number Building Process in DDC: The number building process by using inherent rules in the six tables of DDC.
Table-1: Standard Subdivision:
- Rule-1: General rule: Ordinarily, it always attached to subjects
- First, comes the main class
- and then standard subdivision from table-1
- The accumulation of those two ends up with the desired number.
Example-1: Dictionary of Physics:
|
Main Class |
Physics |
530 |
|
Standard Subdivision |
Dictionary |
-03 |
|
Desired Number |
530.3 | |
Example-2: History of Political Science:
|
Main Class |
Political Science |
320 |
|
Standard Subdivision |
History |
-09 |
|
Desired Number |
320.9 | |
According to the rule of DDC 23rd Edition, our desired number is 320.9 but according to the schedule, our desired number is 320.09.
- Rule-2: (with Political Period): when it comes to historical period-
- First, comes the main class
- Then the range of historical periods followed by the main class.
- Need to write the given instruction
- Then the base number
- and last the given period from table-1
- End up with the desired number.
Example: Economic Condition in 2013:
|
Main Class |
Economic Situation & Condition |
330.9 |
|
Historical Periods |
330.901-905 |
(Add to base number 330.90 the following -090 in notations 0901-0905 from table-1)
|
Base Number |
330.90 |
|
Periods 2013 |
-090512 |
|
Desired Number |
330.9090512 |
Table-2: Areas:
- Rule-1: General rule:
- First, comes the main class
- Then the number of the main class, in specific continents, countries, and localities in the modern world
- then the table of instruction
- Base number
- At last the area notation from table-2
Example: Higher Education in Australia:
|
Main Class |
Higher Education |
378 |
Higher Education in specific continents, countries, and localities in the modern world 378.4-.9
(Add to base number 378 notations 3-9 from table-2)
| Base Number | 378 | |
|
Area |
Australia |
-94 |
|
Desired Number |
378.94 | |
- Rule-2: when there is no area table in the main class, it needs to add “as for instruction -09” with the main class.
Example: Family Planning in Uganda:
|
Main Class |
Family Planning/Birth Control |
363.96 |
| As for instruction | -09 | |
|
Area |
Uganda |
-6761 |
|
Desired Number |
363.96096761 | |
- Rule-3: when it comes to foreign relations and if the country is the motherland then;
- First, comes the main class
- Then it comes to the motherland number
- Add “0”
- At last, it needs to write other country number
Example: Foreign Relation between Bangladesh & India:
| Main Class | Foreign/International Relations | 327 |
Foreign Relation of specific continents, countries, localities 327.3 – .9
(Add to base number 327 notations 3-9 from table-2; then for the relation between that add “0” to the result and notation 1-9 from table-2)
| Base Number | 327 | |
| Area | Bangladesh | -5492 |
| As for Instruction | 0 | |
| Area | India | -54 |
| Desired Number | 327.5492054 | |
- Rule-4: when it comes to foreign relations and if two countries are foreign countries then;
- First, comes the main class
- Then it comes lower notation from the two countries
- Add “0”
- At last, it needs to write other country number
Example: Foreign Relation between Japan & Korea:
| Main Class | Foreign/International Relations | 327 |
Foreign Relation of specific continents, countries, localities 327.3 – .9
(Add to base number 327 notations 3-9 from table-2)
| Base Number | 327 | |
| Area | Korea | -519 |
| As for Instruction | 0 | |
| Area | Japan | -52 |
| Desired Number | 327. 519052 | |
- Rule-5: when one country helps another country then;
- First, comes the main class
- Then it comes which country to help
- Add “0”
- At last, it needs to write the country number that takes the help
Example: American Economic Aid to Bangladesh:
| Main Class | Economic/Foreign Aid | 338.91 |
International assistance by specific jurisdictions and groups of jurisdictions in specific continents, countries, and localities 338.913 – .919
(Add to base number 338.91 notation 3-9 from table-2)
| Base Number | 338.91 | |
| Area | USA | -73 |
| As for Instruction | 0 | |
| Area | Bangladesh | -5492 |
| Desired Number | 338.917305492 | |
- Rule-6: In the migration from one country to another country then;
- First, comes the main class
- Then it comes which country to go
- Add “0”
- At last, it needs to write the number from which country
Example: Migration from Seria to Germany:
| Main Class | Migration | 304.8 |
| Migration | 304.83 – .89 | |
(Add to base number 304.8 notation 3-9 from table-2; then add “0” and to the result and notation from table-2)
| Base Number | 304.8 | |
| Area | Germany | -43 |
| As for Instruction | 0 | |
| Area | Seria | -5694 |
| Desired Number | 304.84305694 | |
- Rule-7: In Emigration from one country to another country then;
- First, comes the main class
- Then it comes to write the number from which country
- Add “-09” (if there is no instruction)
- At last, it needs to write which country to go
Example: Emigration from India to Canada:
| Main Class | Emigration | 325.2 |
Emigration from specific continents, countries, and localities 325.23 – .29
(Add to base number 325.2 notation 3-9 from table-2)
| Base Number | 325.2 | |
| Area | India | -54 |
| As for Instruction | -09 | |
| Area | Canada | -71 |
| Desired Number | 325.2 540971 | |
- Rule-8: In Colonization;
- First, comes the main class
- Then it comes which country stands colony in other country
- As for Instruction “-09” (if there is no instruction)
- At last, it comes to write other country number.
Example: Colonization by the USA to Afghanistan:
| Main Class | Colonization | 325.3 |
Colonization by specific continents, countries, and localities 325.33 – .39
(Add to base number 325.3 notations 3-9 from table-2)
| Base Number | 325.3 | |
| Area | USA | -73 |
| As for Instruction | -09 | |
| Area | Afghanistan | -581 |
| Desired Number | 325.37309581 | |
Table-3: Subdivision of Individual Literature:
- Rule-1: General rule:
- First, comes the main class
- Then come to the standard Subdivision of Individual Literature (SIL)
Example: Bengali Drama:
| Main Class | Bengali Literature | 891.44 |
| SIL | Drama | -1 |
| Desired Number | 891.441 | |
- Rule-2: When it comes to period, then;
- First, comes the main class
- Then comes the standard subdivision of individual literature (SIL)
- Period from table-2
Example: Bengali Poetry in the 21st Century:
| Main Class | Bengali Literature | 891.44 |
| SIL | Drama | -1 |
| Period | 21st Century | 72 |
| Desired Number | 891.44172 | |
Table-4: Subdivision of Individual Language:
- Rule:
- First, comes the main class
- Then comes the standard Subdivision of Individual Language (SIL)
Example-1: Bengali Dictionary:
| Main Class | Bengali Language | 491.44 |
| SIL | Dictionary | -3 |
| Desired Number | 491.443 | |
Example-2: German Pronunciation:
| Main Class | German Language | 430 |
| SIL | Pronunciation | -152 |
| Desired Number | 431.52 | |
Table-5: Ethnic and National Group:
- Rule:
- First, comes the main class
- As for Instruction (-089)
- Nationality
Example: Language of Bengalis:
| Main Class | Language | 400 |
| As for Instruction | -089 | |
| Nationality | Bengali | 9144 |
| Desired Number | 408.99144 | |
Table-6: Language:
- Rule-1:
- First, comes the main class
- Write down the given Instruction
- Base Number
- And Last of all add language
Example: Korean translation into Bengali:
| Main Class | Korean translation | 297.1225 |
(Add to base number 297.1225 notation 1-9 from table-6)
| Base Number | 297.1225 | |
| Language | Bengali | -9144 |
| Desired Number | 297.12259144 | |
- Rule-2: In the case of two languages, then;
- First, comes the less know language as the main class
- Then comes the standard subdivision of individual language (SIL) from table-4
- And last, known language add as language
Example: English to Bengali Dictionary:
| Main Class | English Language | 420 |
| SIL | Dictionary | -3 |
| Language | Bengali | -9144 |
| Desired Number | 423.9144 | |
- Rule-3: If both languages are less known then the language number with greater will be the main class and another will be language.
Example: English to French Dictionary:
| Main Class | French Language | 440 |
| SIL | Dictionary | -3 |
| Language | English | -21 |
| Desired Number | 443.21 | |
- Rule-4: If one language influences another language, in this case;
- The language that influences the other, will be the main class
- As for instruction (-175)
- And last of all, language
Example: Hindi Influence on Bengali:
| Main Class | Hindi Language | 491.43 |
| As for Instruction | -175 | |
| Language | Bengali | -9144 |
| Desired Number | 491.431759144 | |
It is apparent that the Number Building Process is a critical component of the DDC system and plays a vital role in the organization and retrieval of information in libraries. Its hierarchical structure and careful construction provide a powerful framework for effective information management and retrieval.

Library Lecturer at Nurul Amin Degree College