There is a tremendous evolvement in volume in the publication in the form of books, periodicals, journals, etc. It is difficult for scholars to cope with ever-flourishing literature. So, there should be a method to make the maximum literature obtainable for the maximum use at minimum cost. For this reason, literature made tryouts to adopt new techniques. This change brought into effect the work of documentation. In the rest of this article, we are going to discuss documentation is a complete cycle system.
Definition of Documentation:
Since the advent of the term ‘Documentation’ various definitions are being found in library literature.
“Documentation is the process by which are brought together, classified and distributed the documents of all areas of human activity” (Paul Outlet)
“Documentation as a group of techniques which are necessary for organized presentation, organization and communication of information for greater accessibility and utility” (Information Encyclopedia of Information Technology and Library Science)
“Documentation means establishment, identification, collection, and use of document” (ALA Glossary of Library terms)
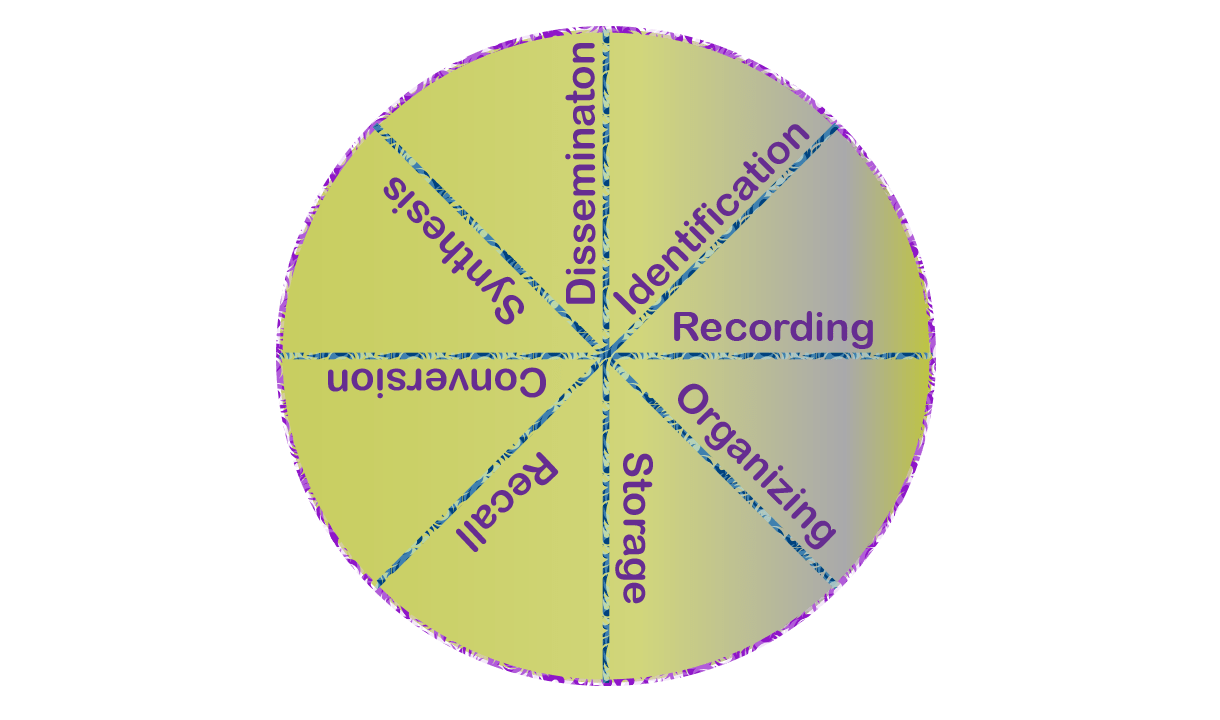
“The documentation is the process of printed or otherwise recorded intellectual activities, which related to identification, recording, organizing, storage, recall, conversion, synthesis and dissemination” (Ralph R. Show)
From the above definitions, we can clarify that documentation is the art of collecting, classifying and making readability accessible the records of all kinds of human activity.
Documentation is a Complete Cycle System:
Documentation is (as viewed by Ralph R. Show) a complete cycle system. Its phases are now discussed:
i. Identification: The first step of the documentation process is to identify the relevant information for the users and to analyze the subject of the information. It should be determined whether the information is of practical utility to the users or not. The following tools may be used for this purpose:
- Catalogues ………. Specially, descriptive and analytical.
- Bibliography ……… Specially, the subject bibliography.
- Abstracts and indexes, and
- Classification, etc.
ii. Recording: The second step of the documentation is to record the selected documents. Documents should be recorded for further use in the future direction and to collect, organize and preserve as complementary of research as well as to assure the use.
Documents can be recorded in variety of ways. Generally, these are recorded according to their subject matter by means of catalogue, index, bibliography, and any other systematic ways. Computers are being used for this purpose in recent times.
iii. Organizing: The success of any service depends upon the promptness and efficiency of its organization, i.e. other activities, documentation requires a well organized. The following points should be considered to make the organizational tasks successful:
- To access the quantity of information.
- To identify how many languages are used to write the documents.
- To determine and evaluate the nature of documents.
- To explain/enlighten the forms of documents.
- To determine and evaluate the qualities relating to publication.
- To determine the criteria for the demonstration of information.
iv. Storage: The pre-requisite of documentation service is the storage of information for use. To ensure the use of information, it can be stored in two main ways:
a.Traditional methods: It includes the following sections:
- Acquisition
- Accession
- Cataloging
- Classification
- Indexing
- Abstracting
- Call Number
- Bibliography
- Typing/labeling
- Shelf arrangement
b. Automated methods: It can be done in two ways which are:
- Reproduction System: It includes;
- Microfilm
- Microfiche
- Photocopy
- Microfilm cartridge
- Ultra fiche
- Aperture card
- Computer-based System: It includes;
- Computer catalog
- Computer microfilm
- Punched Card
- Magnetic tape
- Magnetic drum
- Magnetic core
- Magnetic disc
- Pen-drive
- CD-ROM
- Punch card paper
v. Recall: To recall the required information at the right time is the main purpose of documentation work and service. For recalling information all the methods of storage can be used.
vi. Conversion: Documents are published in different languages. Users are not familiar with all of the languages and forms. So, it is a pre-requisite of documentation to convert documents in a language suitable to users. By these ways to following tasks can be done;
- Translation from one language to another.
- Conversion of the ordinary language of documents in an artificial language.
- Conversion of forms (e.g. micro-forms)
vii. Synthesis: Synthesis is the method of the proper combination between the right documents and users’ interest are mentioned below;
- Content analysis.
- Control on vocabulary and subject analysis.
- Recording the results of the analysis on searchable medium.
- To develop the need analysis and search strategy.
viii. Dissemination: The documentation process ends with the dissemination of information. The degree of success of the documentation process is measured by the efficiency in disseminating information. Various methods are applied to disseminate information. These are;
- Current Awareness Service (CAS)
- Indexing Service
- Abstracting Service
- Selective Dissemination of Information (SDI)
- Bibliographical Services
- Documentation list
- Cataloging and Classification
- Translation Services
- Back-up Services
- Reproduction Services
- Reference Services
- News Clipping Services
It is apparent that documentation is a set of documents provided on paper, or online, or digital, or analog media, such as audio-tape or CDs. Some uses of the documentation still exists and there have been efforts to reintroduce the term as a field of study. That’s really essential to promote our library services.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College