Parts of Computer System:
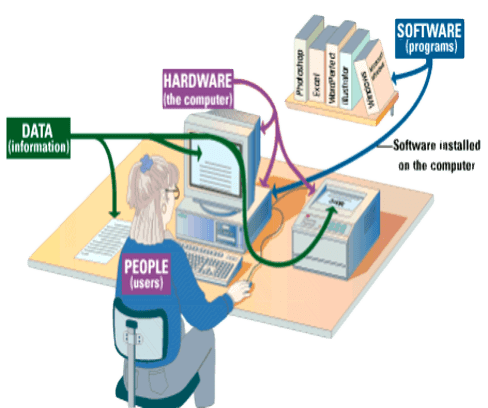
A computer is an electronic device that receives and processes data into information that is useful to people. Parts of the computer system depends on how big it is or how it is used. A complete computer system consists of four parts which are given below;
i. Hardware – physical parts of the computer.
ii. Software – instructions to process the data.
iii. Data – raw facts the computer can process.
-
- Pieces of facts.
- The computer organizes and present information.
iv. People – also known as users/operators.
-
- People operating the computer.
- Computer working for the people.
- Users are the most important part of computers.
- Tell the computer what to do.
Computer Hardware:
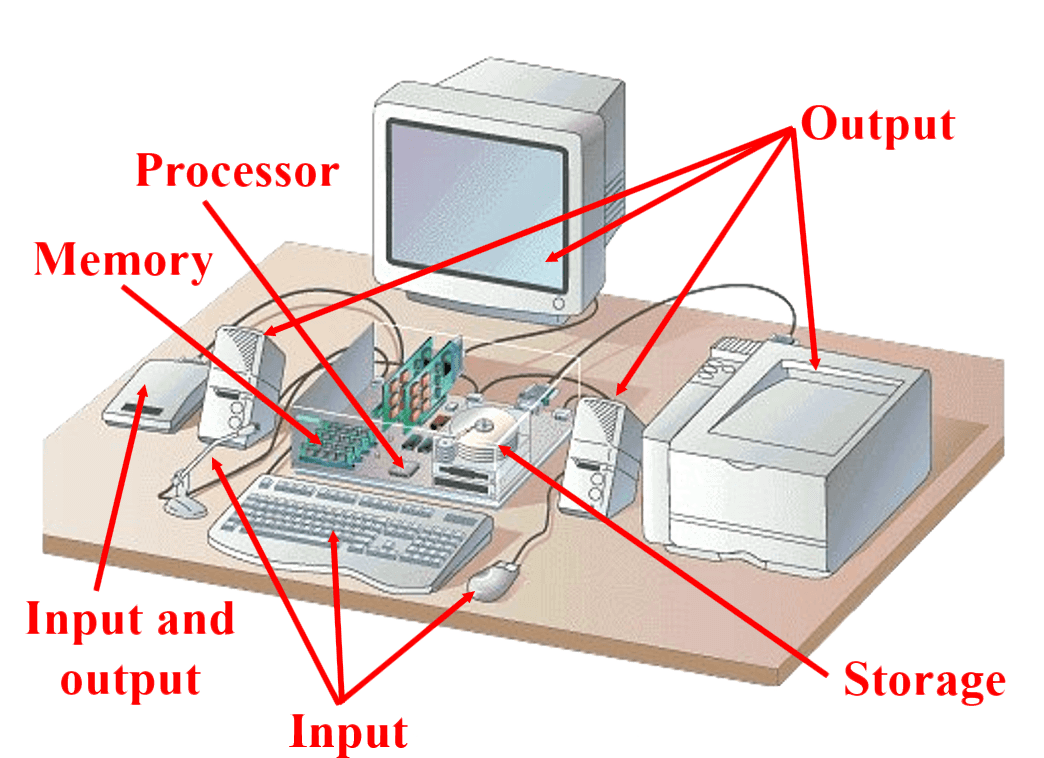
Computer hardware is any physical component of the computer that you can touch. Computer hardware includes the following devices;
- Input and Output Devices: The computer accepts data from some sources (such as the user or a program, for processing) which are called input devices. The computer may be required to display the results of its processing. For example, the results may appear as text, numbers, or a graphic on the computer’s screen or as sounds from its speaker. The computer also can send output to a printer or transfer the output to another computer through a network or the Internet. Output is an optional step in the information processing cycle but may be ordered by the user or program.
- Processor: The processor is like the brain of the computer; it organizes and carries out instructions that come from either the user or the software.
- Memory: In a computer, memory is one or more sets of chips that store data and/or program instructions, temporarily or permanently. Memory is a critical processing component in any computer.
- Storage Devices: The computer permanently stores the results of its processing on a disk, tape, or some other kind of storage medium. As with output, storage is optional and may not always be required by the user or program.
Computer Software:
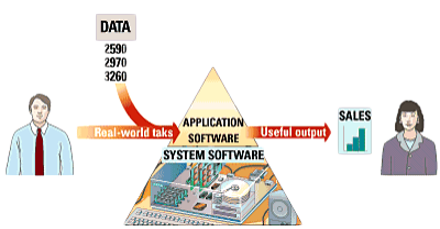
Software is any set of instructions that directs a computer to perform specific tasks or operations. Also known as a “program.” It brings life to the computer.
a. System Software: Enables the application to interact with the computer and manages the computer internal resources.
- Operating System: DOS, Windows, Linux, Unix…
- System Utilities: Driver, Disk clean up, Partition magic
b. Application Software: Performs a general-purpose task.
- Word Processor (MS-Word)
- Spreadsheet (Excel)
- Presentation (PowerPoint)
- Database (Oracle, Access)
- Multimedia, Games
- Website, search engine, etc.
Types of Computers:
⇒Supercomputer: An extremely fast computer that can perform hundreds of millions of instructions per second.
⇒Mainframe: A multi-user computer capable of supporting many hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously.
⇒Minicomputer: A multi-user computer capable of supporting up to hundreds of users simultaneously.
⇒Microcomputer: A small, single-user computer based on a microprocessor.
Types of Micro computers:
- Desktop Computer: The most common type of personal computer is the desktop computer—a PC that is designed to sit on (or under) a desk or table.
- Workstations: A workstation is a specialized, single-user computer that typically has more power and features than a standard desktop PC.
- Notebook Computer: Notebook computers, as their name implies, approximate the shape of an 8.5-by-11-inch notebook and easily fit inside a briefcase.
- Tablet Computer: The tablet PC is the newest development in portable, full-featured computers.
- Handheld Computer: Handheld personal computers are computing devices small enough to fit in your hand.
- Smart Phone: Some cellular phones double as miniature PCs. Because these phones offer advanced features not typically found in cellular phones, they are sometimes called smartphones. These features can include Web and c-mail access, special software such as personal organizers, or special hardware such as digital cameras or music players. Some models even break in half to reveal a miniature keyboard.
References:
- Introduction to Computers by Peter Norton (7th Ed.)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Study Guide by Emmett Dulaney.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College