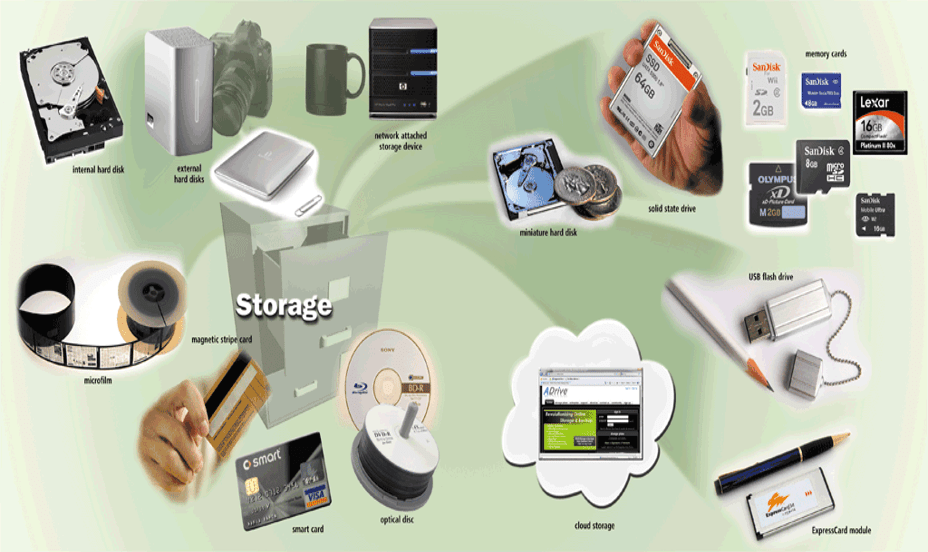
Computer storage devices are the computer hardware’s that records and/or retrieves items to and from storage media. Reading is the process of transferring items from a storage medium into memory. Writing is the process of transferring items from memory to a storage medium.
- Storage holds data, instructions, and information for future use (even when the computer is off).
- A storage medium is a physical material on which a computer keeps data, instructions, and information.
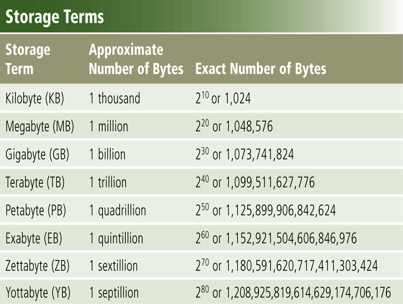
- Capacity is the number of bytes a storage medium can hold Bit, Byte, KB, MG, GB, TB, PB, EB, ZB, YB, etc.
Types of Computer Storage Devices:
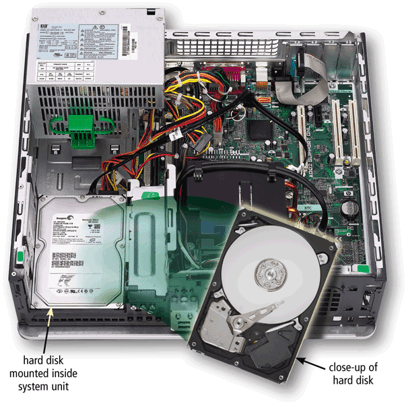
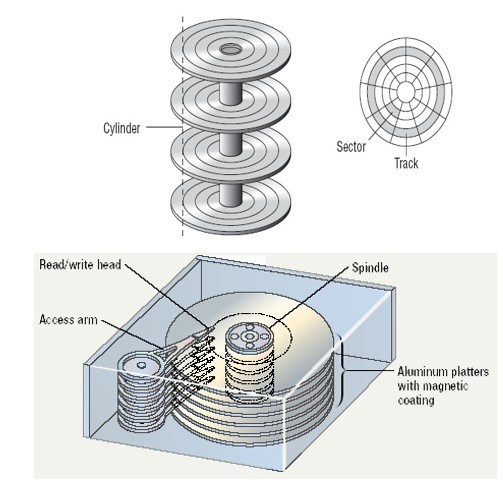
i. Magnetic Storage Device: The device that holds a disk is called a disk drive. A disk is a round, flat object that spins around its center. (Magnetic disks are almost always housed inside a case of some kind, so you can’t see the disk itself unless you open the case.) Read/write heads, which work in much the same way as the heads of a tape recorder or VCR, are used to read data from the disk or write data onto the disk.
-
- HDD, Removable HDD, FDD, Tape drive
- Hard Disks: A hard disk contains one or more inflexible, circular platters that use magnetic particles to store data, instructions, and information.
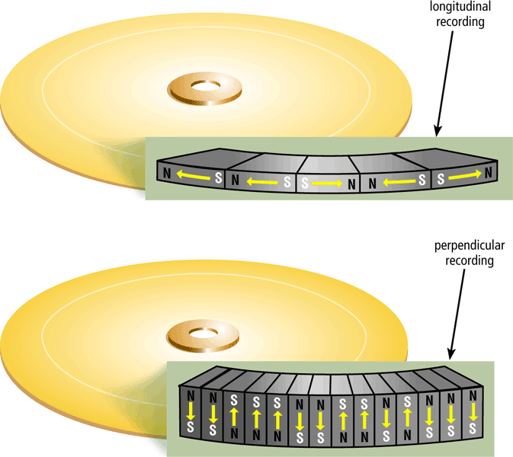
Hard disks can store data using longitudinal recording or perpendicular recording.
-
- Data storage and retrieval:
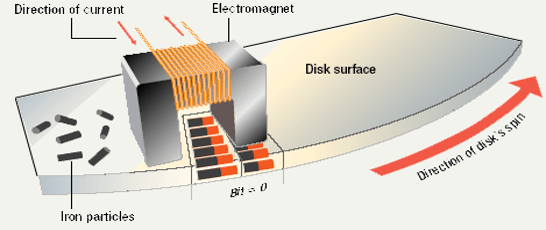
- Media is covered with iron oxide
- Read/write head is a magnet
- Magnet writes charges on the media
- Magnet reads charges
- Drive converts charges into binary
- Data storage and retrieval:
- Components of Hard Drive:
- Platters
- Read/write heads
- Tracks
- Sectors
- (Smallest Unit-512 Bytes)
- Cylinders
- Clusters
- Disk controller
- SATA, EIDE
- SCSI, SAS
- RAID (redundant array of independent disks) is a group of two or more integrated hard disks. The drives can be mirrored so that data written to one of them is also written to others, so if one drive fails, the others just take over.
- A network-attached storage (NAS) device is a server connected to a network with the sole purpose of providing storage [File Server]
- Other Magnetic Storage:
- Removable hard drives plug into the USB port and can be used for backup or transfer of data to another computer.
- Floppy disk drives hold about 1.44 MB of data. They are easily damaged and hence not reliable.
- A tape drive uses a magnetically coated ribbon of plastic, named tape, capable of storing large amounts of data.
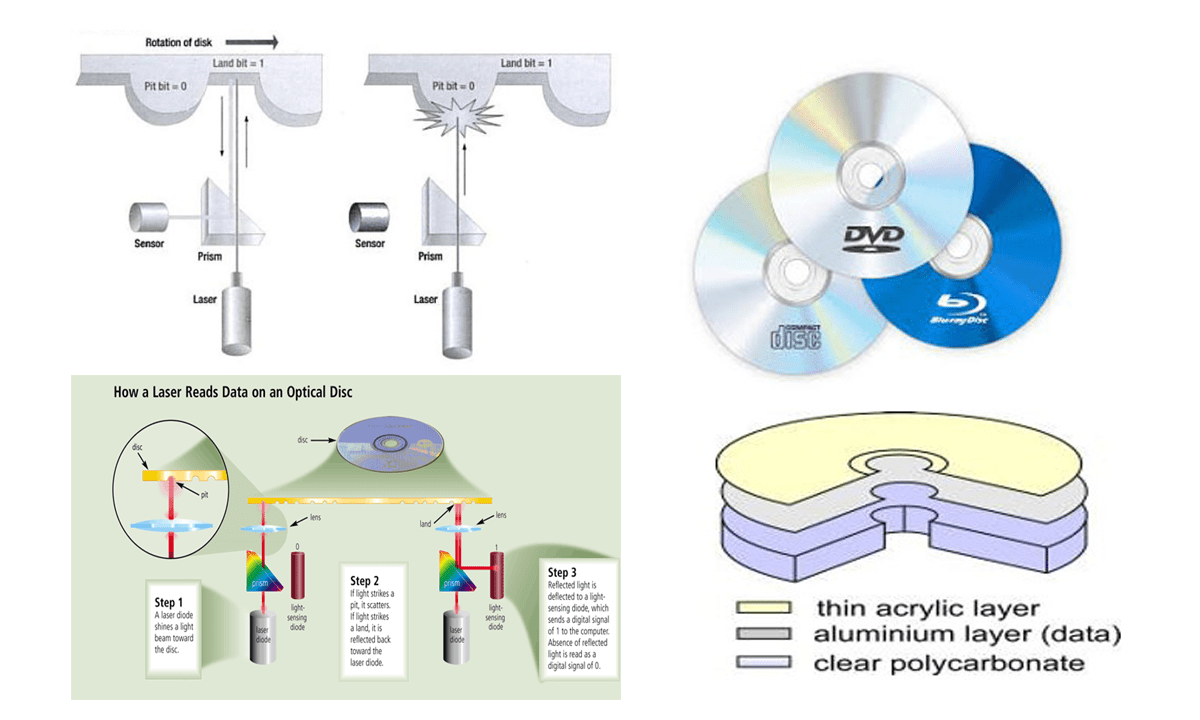
ii. Optical Storage Device: Optical storage devices that use lasers to read data from or write data to the reflective surface of an optical disc. There are three main types:
- Compact Disc (CD)
- 650, 700, 800, 900 MB
- CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW
- Digital Video Disc (DVD)
- SS-SL, SS-DL, DS-SL, DD-DL
- 4.7, 8.5, 9.4, 17.1 GB
- DVD-ROM, DVD-R/DVD+R
- DVD-RW/DVD+RW, DVD-RAM
- Blue-ray Disc (BD)
-
- SS-SL, SS-DL, DS-DL
- 25, 50, 100 GB
- BD-ROM, BD-R, BD-RE
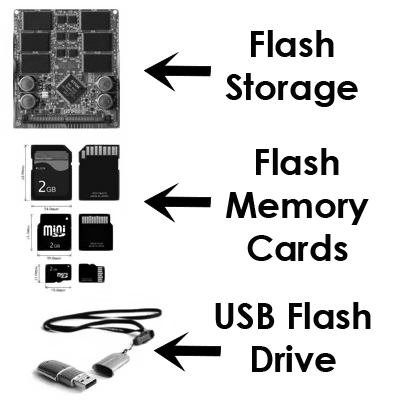
iii. Solid-state Storage Device: Solid-state storage devices are unique among today’s storage devices because they do not use disks or tapes and have no moving parts. Solid-state storage is neither magnetic nor optical, it relies on integrated circuits to hold data. No moving parts, Faster access time, less power consumption, more reliable, long-lasting.
- Flash storage
- BIOS, Modem, Cell phones, Video Game cards, MP3 Player, etc.
- Flash memory cards
- Computer, Camera, Mobile device, etc.
- Compact Flash (CF), Secure Digital (SD)
SD High Capacity (SDHC), Micro SD
- Thumb drive/USB Flash drive
- Plug-in USB port of computer/mobile device
Other Solid-state Storage Device:
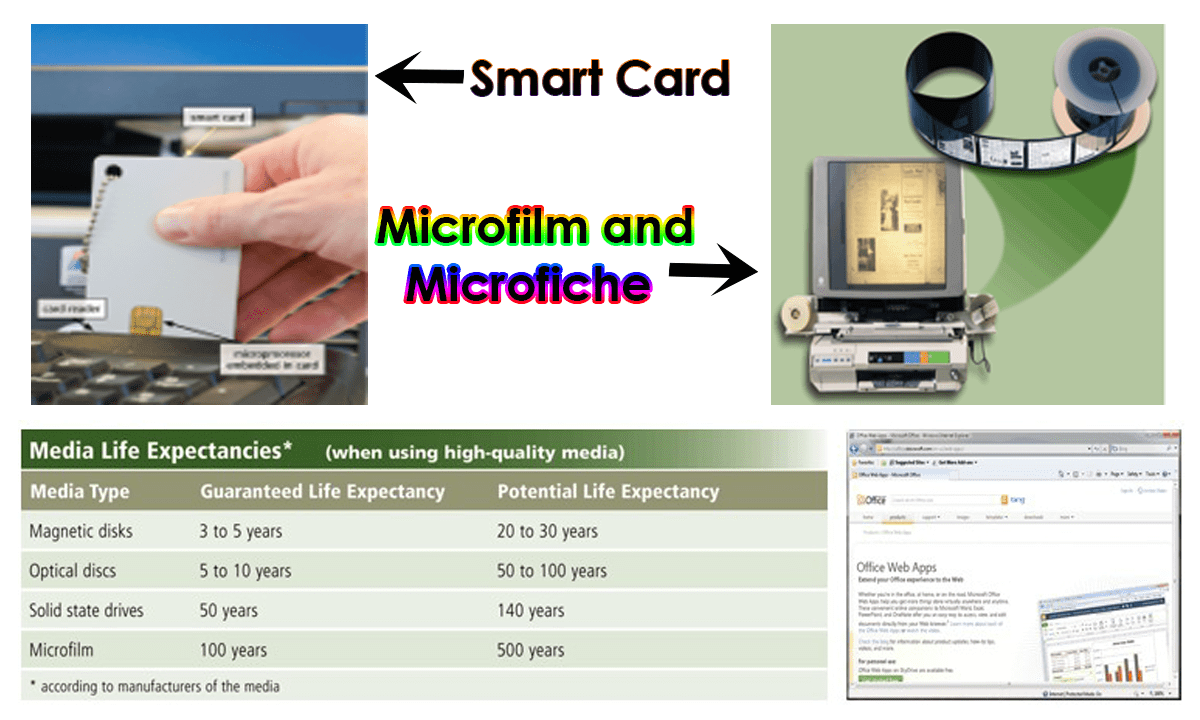
- Smart Card:
- SIM, Credit cards, ID cards
- Microfilm and microfiche:
- Store microscopic images of documents
on a roll or sheet film
- Store microscopic images of documents
- Cloud storage:
-
- Internet service that provides storage to computer users
Drive Performance:
- Average Access Time (Seek Time):
- Time to find desired data
- Measured in milliseconds
- Depends on two factors – RPM – Time to access a track
- The hard drive between 6 and 12 ms
- CD between 80 and 800 ms
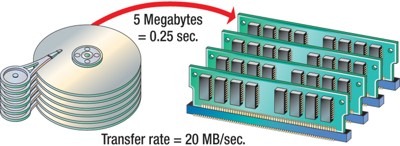
- Data Transfer Rate:
- How fast data can be read
- Measured in Bps or bps
- CD ROMS depend on X factor
- 24x CD transfers 24 x 150 KBps
- The hard drive ranges from 15 to 160 MBps
- Floppy disks transfer at 45 KBps
Optimizing Performance:
Some important computer storage devices optimizing performance are being;
- Clean up unnecessary files:
- Delete temp files
- Delete obsolete data files
- Uninstall unused programs
- Files should be cleaned weekly
- Scan a disk for errors:
- Bad spots on the media
- Find and fix the error
- Move data to a good spot
- Mark the spot as bad
-
- Disks should be scanned monthly
- Defragment a disk:
- Files fragment when resaved
- Fragmented files load slower
- Defragment puts the fragments together
- Disks should be defragged monthly
- File compression:
- Shrinks the size of a file
- Takes up less space on disk
- Reduce the performance of a disk
- Will increase disk capacity
- PKZip, WinZip and WinRAR
References:
- Introduction to Computers by Peter Norton.
- CompTIA A+ Complete Study Guide by Emmett Dulaney.
- http://cs.gsu.edu/~mwang12/Chapter07.ppt
- https://castlecollegeitp.wikispaces.com/file/view/Storage+Devices.ppt

Library Lecturer at Nurul Amin Degree College