An information system (IS) refers to a set of interconnected components that work together to collect, store, process, and disseminate data and information within an organization. It includes hardware, software, data, people, and procedures that are designed to support the operations, management, and decision-making functions of the organization. The main purpose of an information system is to provide timely, accurate, and relevant information to support the activities of an organization. This information may include data about customers, suppliers, employees, products, and services, as well as financial, operational, and strategic data. In this article, we will explore the types of information systems and components of information systems.
Definitions of Information System:
There are several definitions of information systems. Some of them are given below;
“The term information system is a set of people, procedures, and resources that collects transforms, and disseminates information in an organization.” – (James A. O’Brien)
“An information system is a combination of hardware, software, and telecommunications networks that people use to collect, create, and distribute useful data, typically in an organizational context.” (Tech Target)
“An information system is a set of interrelated components that collect, manipulate store data & disseminate information and provide a feedback mechanism to monitor performance.” – (University of Lethbridge Reviews)
“An information system is a system that collects, processes, stores, analyzes, and disseminates data or information for a specific purpose, such as supporting the operations of an organization or facilitating decision-making.” (Encyclopedia Britannica)
“An information system is a computer-based tool that people use to support business operations, management, and decision-making activities. It includes hardware, software, data, and people who work with the system.” (Study.com)
“An information system is an integrated set of components that collect, process, store, and disseminate data and information to support decision-making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualization in an organization.” (Springer Link)
From the above definitions, we can say that an information system is a set of interconnected components that work together to collect, store, process, and disseminate data and information within an organization.
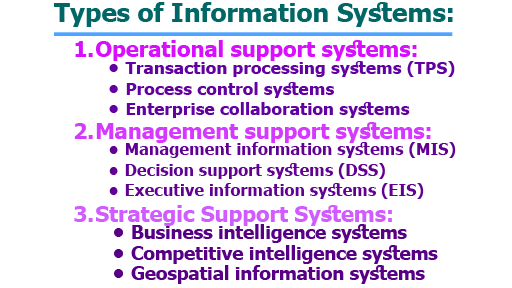
Types of Information Systems:
Information systems can be classified into several categories based on their purpose and the level of management they support. The three main categories of information systems are operational support systems, management support systems, and strategic support systems. These types of information systems are briefly given below;
- Operational support systems: Operational support systems are designed to support the day-to-day operations of an organization. They help organizations to efficiently manage and process large volumes of routine transactions and activities. Examples of operational support systems include:
-
- Transaction processing systems (TPS): These systems are used to process and record routine transactions such as sales, purchases, and payments. They are critical for ensuring the accuracy and timeliness of operational data.
- Process control systems: These systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes, such as manufacturing and chemical processing, to ensure consistent quality and performance.
- Enterprise collaboration systems: These systems are used to facilitate communication and collaboration among employees, customers, and partners. Examples include email, instant messaging, and groupware.
- Management support systems: Management support systems are designed to provide managers with the information they need to make better decisions. They help managers to analyze and understand complex data and to identify trends and patterns that can inform strategic planning. Examples of management support systems include:
-
- Management information systems (MIS): These systems provide managers with reports and analyses of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to the organization’s operations. They are used to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Decision support systems (DSS): These systems provide managers with tools and analysis to help them make complex decisions. They use advanced analytical techniques to model and simulate different scenarios, and to identify the best course of action.
- Executive information systems (EIS): These systems provide senior executives with a high-level overview of the organization’s performance. They are used to monitor trends and identify strategic opportunities and risks.
- Strategic Support Systems: Strategic support systems (also known as executive support systems) are a type of information system that is designed to support senior management in making strategic decisions. These systems provide executives with access to critical information from both internal and external sources, allowing them to analyze trends and identify strategic opportunities and risks. Examples of strategic support systems include:
-
- Business intelligence systems: These systems provide executives with access to real-time data from across the organization, allowing them to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Competitive intelligence systems: These systems provide executives with insights into the activities and strategies of competitors, helping them to anticipate competitive threats and identify opportunities for differentiation.
- Geospatial information systems: These systems provide executives with access to location-based data, allowing them to analyze market trends and identify potential opportunities and risks in different regions.
Components of Information Systems:
An information system (IS) is composed of several components that work together to process, store, and disseminate information. The main components of an information system are:
a. People resources: People are the most critical component of an information system. They are the users, designers, developers, and maintainers of the system. They determine the success or failure of the system. People resources include end-users, system administrators, developers, and other stakeholders.
b. Hardware resources: Hardware resources include machines and media that are used to process and store information. Machines: Computers, video monitors, magnetic disk drives, printers, optical scanners, etc. & Media: Floppy disks, magnetic tapes, pen drives, CDROMs, etc.
c. Software resources: Software resources include the programs and applications that run on the hardware components. This includes operating systems, programming languages, application software, and system software. Software resources are used to manage, process, and analyze data.
d. Data resources: Data resources include databases, knowledge bases, and model bases. Databases are collections of structured data that are organized and stored for easy access and retrieval. Knowledge bases are collections of knowledge and expertise that are used to support decision-making processes. Model bases are mathematical models that are used to simulate and analyze real-world systems.
e. Network resources: Network resources include communication media and network support. Communication media include cables, wires, and wireless devices that are used to connect computers and other devices. Network support includes protocols and standards that are used to manage and control the flow of information over the network.
f. Information products or product resources: Information products or product resources include reports, analyses, and other outputs that are generated by the system. These products are used by decision-makers to support their decision-making processes. Information products can be in the form of text, graphics, audio, or video.
In conclusion, information systems are an integral part of modern organizations, as they provide valuable support for decision-making, communication, and collaboration. These systems range from simple tools, such as spreadsheets and email, to complex enterprise resource planning systems, which integrate various business processes. A well-designed information system can provide a competitive advantage to organizations by facilitating faster and more accurate decision-making, improving communication and collaboration among employees, and increasing operational efficiency.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College