Key Principles of Management:
Principles of management serve as the bedrock upon which successful organizations are built. These principles, formulated through years of observation, study, and practice, provide a structured approach to guiding managerial decisions, actions, and strategies. As foundational guidelines, they enable managers to navigate complexities, optimize resources, and achieve organizational objectives. This article delves into the key principles of management, delving deeper into their significance, application, and profound impact on organizational effectiveness.
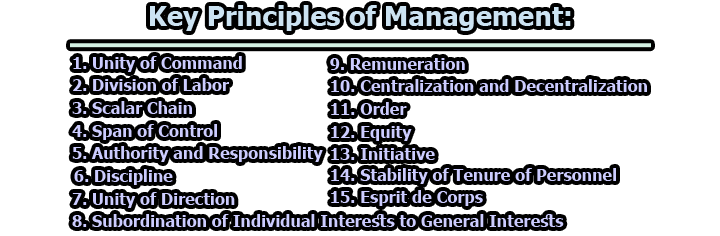
1. Unity of Command: The principle of unity of command emphasizes the importance of a clear and singular line of authority. Each employee should report to only one supervisor or manager to avoid confusion, conflicting instructions, and divided loyalties. This principle ensures that employees know exactly who to report to, where accountability lies, and where to seek guidance. By adhering to this principle, organizations prevent the chaos that can arise from multiple supervisors and maintain a structured and efficient chain of command.
2. Division of Labor: The division of labor principle, popularized by Adam Smith, emphasizes specialization in tasks. It posits that breaking down complex tasks into smaller, specialized components improves efficiency and productivity. Specialization allows employees to develop expertise in specific areas, perform tasks faster, and reduce the learning curve. Organizations embracing this principle experience streamlined processes, reduced production time, and greater output. However, an overemphasis on the division of labor may lead to employee dissatisfaction and monotony, so a balanced approach is essential.
3. Scalar Chain: The scalar chain principle recognizes the hierarchical structure of authority within organizations. It dictates a clear flow of communication and decision-making, moving from top management down to the frontline employees. This principle ensures that information is communicated efficiently, decisions are implemented effectively, and organizational goals are cascaded throughout the hierarchy. A well-established scalar chain minimizes delays, miscommunication, and misunderstandings, facilitating cohesive operations.
4. Span of Control: The span of control principle addresses the optimal number of subordinates a manager can effectively supervise. It acknowledges that a manager’s efficiency diminishes as the number of subordinates increases. Determining the appropriate span of control involves considering factors such as the complexity of tasks, employee capabilities, and the manager’s leadership skills. A wider span of control promotes flatter organizational structures, fosters empowerment among employees, and enhances decision-making agility. Conversely, a narrower span of control provides more hands-on supervision but can lead to excessive layers of hierarchy.
5. Authority and Responsibility: This principle establishes a crucial link between authority and responsibility. Authority, the power to make decisions, must align with the corresponding level of responsibility, the obligation to execute tasks, and achieve objectives. Effective management ensures that authority is commensurate with the scope of responsibility. Managers should possess the necessary authority to make informed decisions while being accountable for their outcomes. This alignment fosters efficient decision-making, accountability, and clarity in roles.
6. Discipline: Discipline is a cornerstone principle that ensures a harmonious and productive work environment. It calls for employees to adhere to established rules, norms, and codes of conduct. Managers play a pivotal role in fostering discipline by setting clear expectations, enforcing policies consistently, and addressing deviations promptly. A disciplined workplace minimizes conflicts, enhances orderliness, and upholds the organization’s values. However, discipline should be balanced with flexibility and understanding to maintain employee morale.
7. Unity of Direction: The unity of direction principle emphasizes the importance of aligning efforts toward a common goal. All employees should work cohesively toward shared objectives, driven by a unified vision and strategy. This principle prevents conflicting priorities, promotes synergy among departments, and channels resources toward common goals. By ensuring a singular direction, management creates a focused, efficient, and collaborative organizational culture.
8. Subordination of Individual Interests to General Interests: This principle emphasizes the primacy of the organization’s interests over individual agendas. It encourages employees to prioritize the collective good over personal gains. Management fosters this alignment by cultivating a sense of ownership and shared purpose among employees. Organizations that uphold this principle promote teamwork, reduce conflicts arising from self-interest, and create an environment where the success of the whole takes precedence.
9. Remuneration: The remuneration principle recognizes the significance of fair compensation for employees’ contributions. Adequate and equitable remuneration motivates employees, increases job satisfaction, and reduces turnover. Effective management ensures that compensation aligns with industry standards, job responsibilities, and employee performance. Beyond monetary rewards, remuneration includes non-financial incentives such as recognition, career advancement opportunities, and a positive work environment.
10. Centralization and Decentralization: Centralization and decentralization address the distribution of decision-making authority within an organization. Centralization consolidates decision-making at higher management levels, promoting consistency and control. Decentralization delegates decision-making to lower levels, fostering empowerment and responsiveness. The balance between these approaches depends on the organization’s size, complexity, and culture. Centralization ensures consistency, while decentralization encourages innovation, adaptability, and quicker responses to local challenges.
11. Order: The ordering principle encompasses both material and human resources. It pertains to the organization of workspaces, resources, and tasks. Management ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, work processes are streamlined, and responsibilities are clearly defined. A well-organized workplace reduces wasted time, enhances productivity, and contributes to a conducive environment for efficient operations.
12. Equity: The equity principle emphasizes fairness and impartiality in organizational policies and decisions. It demands that all employees be treated equitably, regardless of factors such as gender, ethnicity, or personal affiliations. Management establishes equitable policies for hiring, promotions, compensation, and disciplinary actions. An equitable workplace fosters trust, reduces grievances, and promotes diversity and inclusion.
13. Initiative: The initiative principle encourages employees to take proactive steps to improve processes and contribute to innovation. Effective management cultivates an environment where employees are empowered to suggest improvements, propose new ideas, and take calculated risks. Encouraging initiative nurtures a culture of creativity, continuous improvement, and adaptability. Organizations that value initiative benefit from employee engagement, enhanced problem-solving, and a culture of innovation.
14. Stability of Tenure of Personnel: Stability of tenure recognizes the importance of retaining skilled employees. High turnover disrupts operations, hampers knowledge retention, and affects organizational culture. Effective management offers job security, opportunities for growth, and a positive work environment. By fostering stability, organizations reduce recruitment costs, maintain institutional knowledge, and create a committed workforce.
15. Esprit de Corps: Esprit de corps emphasizes team spirit, camaraderie, and collaboration among employees. Effective management fosters a positive workplace culture that values teamwork, open communication, and mutual support. Organizations that prioritize esprit de corps create an environment where employees feel motivated, engaged, and aligned with the organization’s mission. This principle enhances employee morale, reduces conflicts, and promotes a sense of belonging.
In conclusion, the key principles of management form a dynamic framework that guides managers in making informed decisions, leading teams, and achieving organizational goals. These principles are not rigid rules but rather adaptable guidelines that consider various contexts, cultures, and challenges. By embracing these principles, management fosters efficient operations, a positive work culture, and sustainable growth. Balancing these principles in a manner aligned with the organization’s values and objectives enhances managerial effectiveness and contributes to the overall success of the organization.

Former Student at Rajshahi University