Seven Fundamental Principles of Marketing Management:
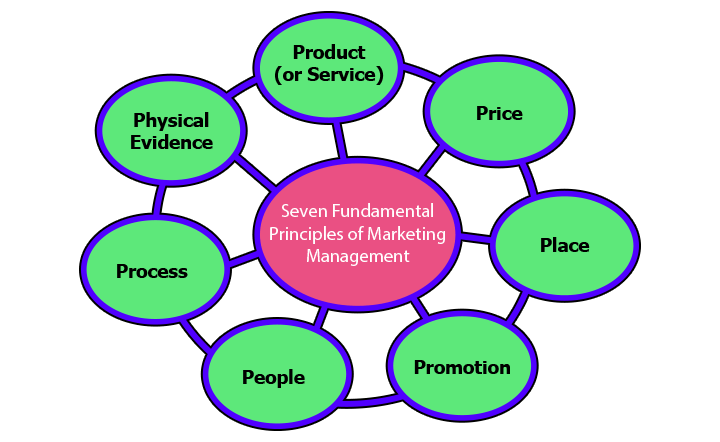
In the dynamic landscape of business, effective marketing management is essential for organizations to thrive. The principles of marketing provide a framework that guides businesses in their efforts to understand customer needs, create valuable products or services, set appropriate prices, distribute products efficiently, promote effectively, manage people, streamline processes, and establish a credible physical presence. Here, we are going to explore the seven fundamental principles of marketing management and see the sights their significance in achieving overall business success.
1. Product (or Service): The foundation of marketing begins with the product or service itself. Businesses must meticulously design, develop, and deliver offerings that meet the needs and wants of their target audience. This involves understanding consumer preferences, conducting market research, and continually innovating to stay ahead of the competition.
For a product, marketers must consider features, quality, design, branding, and packaging. On the other hand, service-oriented businesses focus on aspects such as reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and tangibles. In both cases, creating a unique selling proposition (USP) helps distinguish the product or service in a crowded market.
2. Price: Pricing is a delicate balance between generating revenue and providing value to customers. Determining the right price involves considering production costs, competitor pricing, perceived value, and the overall economic environment. Pricing strategies may include penetration pricing to gain market share, skimming to capitalize on exclusivity, or value-based pricing tied to the perceived benefits of the product or service.
Dynamic pricing models, discounts, and bundling are additional tools at a marketer’s disposal. It’s crucial to understand that pricing is not a one-time decision; it requires continuous evaluation and adjustment to align with market conditions and consumer expectations.
3. Place: The ‘Place’ element focuses on making products or services accessible to consumers at the right time and location. This involves selecting appropriate distribution channels, establishing efficient logistics, and managing inventory effectively. For physical products, considerations include selecting the right retail partners, determining optimal shelf placements, and managing transportation and warehousing.
In the digital age, e-commerce and online presence play a pivotal role in place strategy. Businesses need to understand where their target audience shops and ensure their products or services are available through those channels, whether online or offline.
4. Promotion: Promotion encompasses all activities aimed at creating awareness, generating interest, and driving sales. It includes advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and personal selling. The goal is to communicate the value proposition of the product or service to the target audience effectively.
Integrated marketing communication (IMC) ensures consistency across all promotional activities. Social media, content marketing, influencer partnerships, and traditional advertising channels are leveraged based on the nature of the product and the preferences of the target market.
5. People: In the context of marketing, the ‘People’ principle recognizes the critical role of employees, both frontline and behind the scenes. Employees are the face of the organization, directly influencing customer experience and satisfaction. Proper training, motivation, and alignment with the brand values are crucial to ensure employees represent the company positively.
Moreover, the principle extends beyond internal staff to include external stakeholders, such as suppliers and partners. Building strong relationships with all parties involved contributes to a positive brand image and enhances the overall customer experience.
6. Process: Efficient processes are essential to delivering a seamless customer experience from product selection to post-purchase support. This principle involves streamlining internal operations, minimizing bottlenecks, and ensuring consistency in delivering products or services.
Automation, technology integration, and continuous process improvement are integral components of an effective marketing strategy. By focusing on the customer journey, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize processes to enhance overall satisfaction.
7. Physical Evidence: The ‘Physical Evidence’ principle refers to the tangible and intangible cues that influence customer perceptions about a product or service. This includes the physical environment in which a service is delivered, as well as the packaging, branding, and quality of a product. Physical evidence contributes to building trust and credibility.
In the digital era, website design, user interface, and online reviews also fall under the purview of physical evidence. Creating a consistent and positive impression across all touchpoints reinforces the brand image and contributes to customer loyalty.
In conclusion, the seven principles of marketing management serve as a comprehensive guide for businesses aiming to succeed in a competitive marketplace. By focusing on product development, pricing strategies, distribution channels, promotional activities, people management, efficient processes, and physical evidence, organizations can create a holistic marketing approach that resonates with their target audience.
Adapting these principles to the ever-changing business landscape requires continuous monitoring, analysis, and adaptation. The integration of technology and data analytics further enhances the ability of businesses to understand consumer behavior and market trends, allowing for more informed decision-making.
Successful marketing management is an ongoing process that requires agility, creativity, and a deep understanding of both the market and the target audience. By embracing these principles, businesses can build strong, customer-centric strategies that foster growth and sustainability in today’s dynamic business environment.

Assistant Teacher at Zinzira Pir Mohammad Pilot School and College