Importance of Tourism Management:
Tourism is one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing industries, contributing significantly to the global economy. As a multifaceted sector, tourism involves a wide range of services, including transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, and entertainment. Managing these services efficiently is essential to ensure a seamless experience for travelers, while also fostering sustainable economic and social benefits for local communities. Tourism management refers to the strategic planning, development, and oversight of tourism activities, aiming to maximize the benefits while minimizing potential negative impacts. The importance of tourism management extends beyond creating a pleasurable experience for tourists—it plays a crucial role in economic development, cultural preservation, and environmental conservation.
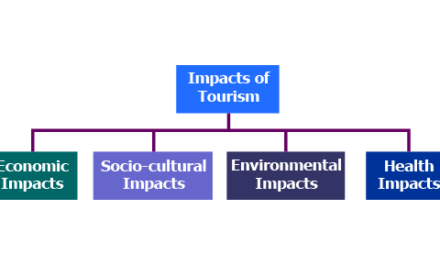
1. Economic Growth and Job Creation: Tourism is a major economic driver for many countries, especially developing nations. Effective tourism management ensures that tourism activities contribute to local economies by generating income and creating jobs. A well-managed tourism sector provides direct employment in hotels, travel agencies, airlines, and restaurants, as well as indirect jobs in industries like construction, agriculture, and retail. This helps alleviate poverty and boost local economies, especially in rural and remote areas.
2. Sustainable Development: Sustainable tourism is at the core of modern tourism management. Tourism management encourages practices that minimize environmental degradation, conserve natural resources, and respect local cultures. By promoting eco-friendly tourism initiatives, such as wildlife conservation projects and green hotel practices, tourism managers can help ensure that tourism activities do not compromise the ability of future generations to enjoy the same natural and cultural resources.
3. Infrastructure Development: Tourism management drives the development of essential infrastructure, such as transportation, communication, and utilities. Investments in roads, airports, water supply, and sanitation systems are often spurred by the need to accommodate tourists. These improvements benefit not only visitors but also local residents, enhancing their quality of life and contributing to broader national development.
4. Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Cultural tourism is a growing trend, with many travelers seeking authentic experiences that immerse them in the history, traditions, and arts of a destination. Tourism management helps preserve and promote cultural heritage by supporting initiatives that protect historical sites, museums, festivals, and local customs. This preservation not only attracts tourists but also fosters pride among local communities and ensures that their cultural identity is passed on to future generations.
5. Environmental Conservation: In many regions, tourism management is closely tied to environmental conservation. Nature-based tourism, such as wildlife safaris, hiking, and diving, depends on the preservation of natural habitats. Tourism managers play a key role in ensuring that these activities are conducted responsibly, with minimal harm to the environment. By implementing policies that reduce waste, conserve water, and protect ecosystems, tourism management helps safeguard biodiversity and natural landscapes for both tourism and conservation purposes.
6. Diversification of Economies: For various countries, tourism management provides an opportunity to diversify their economies. In regions that are heavily reliant on agriculture, mining, or manufacturing, the development of a robust tourism sector can provide alternative sources of income. This diversification helps buffer economies against fluctuations in other sectors and creates resilience, especially in times of economic downturns or global crises.
7. Crisis Management and Risk Mitigation: Tourism is highly vulnerable to crises, including natural disasters, political instability, and pandemics. Effective tourism management is critical for preparing for and responding to such crises. Tourism managers develop contingency plans, implement safety protocols, and provide clear communication during emergencies to ensure the safety of tourists and protect the reputation of destinations. These efforts help minimize the long-term damage to tourism industries and facilitate quicker recovery.
8. Enhanced Visitor Experience: One of the core objectives of tourism management is to enhance the visitor experience. By managing attractions, accommodations, transportation, and customer service effectively, tourism managers ensure that visitors enjoy a seamless and memorable stay. This leads to higher levels of tourist satisfaction, repeat visits, and positive word-of-mouth recommendations, all of which contribute to the long-term success of a destination.
9. Strengthening International Relations: Tourism fosters cultural exchange and understanding between people from different parts of the world. Through tourism management, countries can promote themselves as welcoming, diverse, and safe destinations. This soft power helps build positive international relations and strengthens diplomatic ties. Moreover, by engaging in global tourism networks and adhering to international standards, countries enhance their reputation on the global stage.
10. Contribution to Global Knowledge and Research: Tourism management contributes to a growing body of knowledge and research that helps shape global tourism policies and practices. Universities and research institutions collaborate with tourism managers to study trends, assess impacts, and develop strategies that benefit both the industry and society. The insights gained from these studies inform decision-making at the local, national, and international levels, promoting best practices in sustainability, crisis management, and economic development.
It is apparent that tourism management is a vital component of the global tourism industry. It ensures that tourism not only provides enjoyable experiences for travelers but also delivers lasting economic, social, and environmental benefits for destinations and local communities. By fostering sustainable development, preserving cultural and natural resources, and mitigating risks, tourism management enhances the long-term viability and success of the tourism sector. In a world where tourism continues to grow and evolve, the role of tourism management becomes increasingly important in promoting coexistence between tourism, communities, and the environment.

Library Lecturer at Nurul Amin Degree College